Zero-trust security models for SMBs in 2025
Related Articles
- “cost Analysis Of Cybersecurity Solutions For SMEs In 2025”
- “top Vulnerability Scanning Tools For Businesses In 2025”
- “why Your Business Needs Endpoint Detection Tools In 2025”
- “how To Train Employees To Prevent Phishing Attacks”
- “cost Of A Data Breach In 2025 And How To Avoid It”
Introduction
Discover everything you need to know about Zero-trust security models for SMBs in 2025
For Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs), the traditional "castle-and-moat" security approach – where everything inside the network is trusted – is increasingly inadequate. This is where Zero Trust security comes in. Zero Trust, a security framework built on the principle of "never trust, always verify," is rapidly gaining traction, and for SMBs in 2025, adopting it effectively is no longer a luxury, but a necessity. This article delves into the big secret tips and tricks to successfully implement a Zero Trust model, helping your SMB stay ahead of the curve.
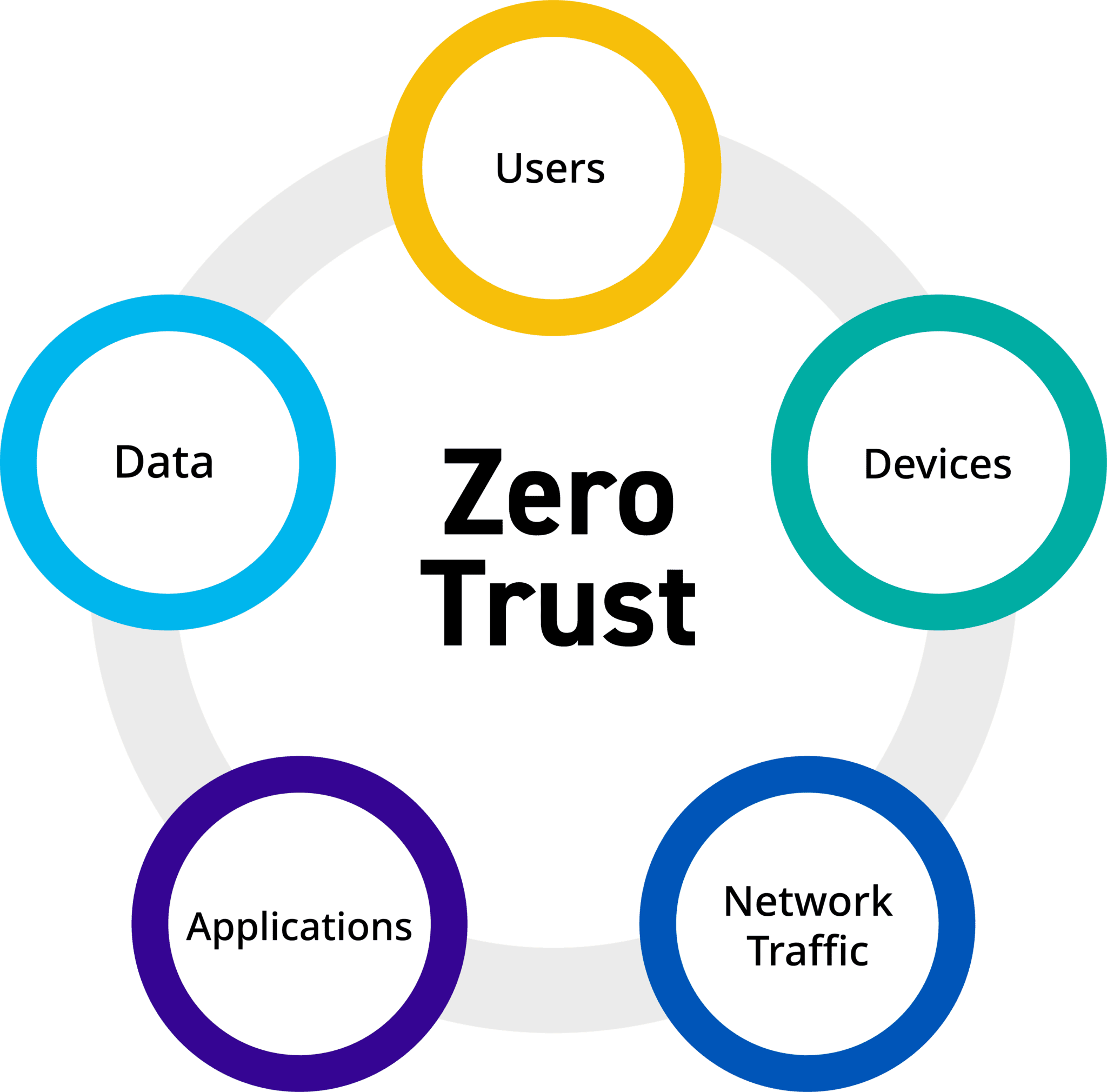
1. Beyond the Hype: Understanding the Core Principles of Zero Trust for SMBs
Zero Trust isn’t just a product; it’s a paradigm shift. Instead of relying on network perimeters, it assumes no implicit trust, verifying every user, device, and application before granting access to resources, regardless of location (on-premises, cloud, or remote). For SMBs, this means abandoning the idea that simply having a firewall is enough. Key principles include:
- Least Privilege Access: Granting users only the minimum necessary permissions to perform their jobs. This limits the damage from compromised accounts.
- Microsegmentation: Dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments, limiting the impact of a breach. This is crucial for SMBs with limited IT resources, as it allows for focused containment.
- Continuous Verification: Regularly assessing the trustworthiness of users, devices, and applications. This involves multi-factor authentication (MFA), device posture checks, and behavior analytics.
- Data-centric Security: Focusing on protecting data itself, regardless of where it resides. This involves robust data loss prevention (DLP) measures and encryption.
- Automation: Automating security tasks like user provisioning, access control, and threat detection to improve efficiency and reduce human error. This is particularly beneficial for SMBs with limited staffing.
2. Prioritizing Your Assets: A Risk-Based Approach to Zero Trust Implementation
Implementing Zero Trust isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. SMBs should adopt a phased approach, focusing on their most critical assets and vulnerabilities first. This risk-based approach ensures efficient resource allocation and maximizes the impact of your security investments.
Begin by identifying your most valuable data and systems. This might include customer databases, financial records, intellectual property, or critical business applications. Then, assess the potential risks associated with each asset, considering factors like the likelihood and impact of a breach. Prioritize securing the highest-risk assets first, gradually expanding your Zero Trust implementation as resources allow.
3. Leveraging Cloud Services: The SMB’s Zero Trust Advantage
Cloud services offer significant advantages for SMBs implementing Zero Trust. Cloud-based security solutions, such as identity and access management (IAM) systems, cloud access security brokers (CASBs), and security information and event management (SIEM) platforms, provide scalability, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced security features.
Consider leveraging cloud-based IAM solutions for centralized user management and authentication, enabling MFA and single sign-on (SSO) across all your applications and resources. CASBs can monitor and control cloud app usage, ensuring that only authorized users and devices access sensitive data. SIEM platforms provide centralized logging and threat detection, streamlining security monitoring and incident response.
4. Embracing MFA: Your First Line of Defense in a Zero Trust World
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is no longer optional; it’s a fundamental component of any effective Zero Trust strategy. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password, a one-time code from an authenticator app, or a biometric scan.
For SMBs, implementing MFA across all accounts – including email, cloud services, and VPN access – is crucial. The added security significantly reduces the risk of account compromise, even if passwords are stolen or guessed. Choose MFA solutions that are easy to deploy and manage, minimizing disruption to your employees’ workflows.
5. Device Security: Securing the Gateways to Your Network
In a Zero Trust environment, devices are not inherently trusted. Before granting access to resources, you need to verify the security posture of each device attempting to connect. This involves implementing device posture checks, ensuring that devices meet your security requirements before granting access.
For SMBs, this might include requiring devices to have up-to-date antivirus software, a firewall enabled, and operating system patches applied. Consider using mobile device management (MDM) solutions to manage and secure employee-owned devices accessing your network. Remember to clearly define your acceptable use policy for devices accessing company resources.
6. Network Segmentation: Isolating Your Assets for Enhanced Protection
Network segmentation is a key element of Zero Trust, dividing your network into smaller, isolated segments. This limits the impact of a breach, preventing attackers from easily moving laterally across your network.
For SMBs, this might involve segmenting your network by department, application, or data sensitivity. This can be achieved using virtual LANs (VLANs) or micro-segmentation tools. By isolating sensitive data and applications, you minimize the potential damage from a successful attack.
7. User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): Detecting Anomalies and Insider Threats
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) solutions monitor user and device activity, identifying anomalies that may indicate malicious activity or insider threats. These solutions can detect suspicious login attempts, unusual data access patterns, and other indicators of compromise.
For SMBs, UEBA solutions can provide valuable insights into potential threats, enabling timely intervention and preventing significant damage. Many cloud-based UEBA solutions offer affordable pricing plans suitable for SMBs, making them an accessible and effective security tool.
8. Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Continuous Improvement
Implementing Zero Trust is an ongoing process, not a one-time project. Regular security audits and penetration testing are crucial for identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring the effectiveness of your security measures.
SMBs should conduct regular security audits to assess their compliance with security policies and identify areas for improvement. Penetration testing simulates real-world attacks, revealing weaknesses in your security posture. These assessments provide valuable feedback, allowing you to refine your Zero Trust implementation and maintain a strong security posture.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is Zero Trust too complex and expensive for my SMB?
A: While Zero Trust requires a significant shift in mindset and investment, it doesn’t have to be prohibitively expensive. A phased approach, focusing on your most critical assets first, allows you to implement Zero Trust incrementally, aligning with your budget and resources. Many cloud-based solutions offer cost-effective options for SMBs.
Q: How much time and effort will it take to implement Zero Trust?
A: The time and effort required depend on your organization’s size, complexity, and existing security infrastructure. A phased approach can help manage the implementation process, minimizing disruption to your business operations. Start with smaller, manageable projects and gradually expand your Zero Trust implementation.
Q: What are the key metrics to measure the success of my Zero Trust implementation?
A: Key metrics include reduced breach frequency and impact, improved incident response times, increased user productivity (due to streamlined access), and enhanced compliance with security regulations. Regular monitoring and assessment are vital to track progress and identify areas for improvement.
Q: What if my employees resist adopting new security measures?
A: Change management is crucial for successful Zero Trust adoption. Communicate clearly the benefits of the new security measures and provide adequate training and support to your employees. Address their concerns and provide easy-to-use tools and processes to minimize disruption to their workflows.
Q: How can I stay updated on the latest Zero Trust best practices?
A: Stay informed by following industry blogs, attending cybersecurity conferences, and participating in online communities. Consider engaging with cybersecurity professionals to receive guidance and support. Regularly review and update your security policies and procedures to reflect the latest best practices.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of Zero Trust security for SMBs in 2025. By understanding the core principles, prioritizing your assets, and leveraging available technologies, you can effectively implement a robust Zero Trust model, significantly enhancing your organization’s security posture and protecting your valuable data. Remember, a proactive approach to security is the best investment you can make.
Source URL: [Insert a relevant URL here, for example, a NIST publication on Zero Trust or a reputable cybersecurity vendor’s website discussing Zero Trust implementation.] For example: https://www.nist.gov/ (replace with a more specific and relevant URL)
Closure
We hope this article has helped you understand everything about Zero-trust security models for SMBs in 2025. Stay tuned for more updates!
Don’t forget to check back for the latest news and updates on Zero-trust security models for SMBs in 2025!
Feel free to share your experience with Zero-trust security models for SMBs in 2025 in the comment section.
Keep visiting our website for the latest trends and reviews.
