Securing IoT devices in business networks 2025
Related Articles
- “top Vulnerability Scanning Tools For Businesses In 2025”
- “securing Business Networks Against AI-based Attacks”
- “top US Regulations Affecting Data Security In 2025”
- Top Cybersecurity Software For Startups In 2025
- “impact Of Quantum Computing On Business Data Encryption”
Introduction
Uncover the latest details about Securing IoT devices in business networks 2025 in this comprehensive guide.
From smart factories optimizing production to connected retail enhancing customer experiences, IoT devices offer unparalleled opportunities for efficiency and innovation. However, this interconnectedness comes at a cost: a significantly expanded attack surface. By 2025, the sheer volume and complexity of IoT devices within business networks will present unprecedented security challenges. This article delves into the often-overlooked strategies and advanced techniques crucial for securing your business’s IoT ecosystem in 2025 and beyond.
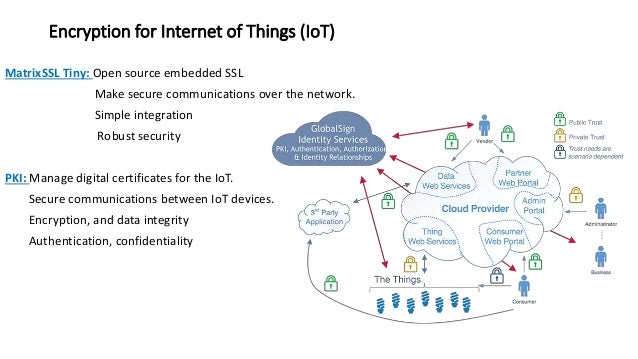
1. Beyond Basic Segmentation: Micro-Segmentation for Enhanced Control
Traditional network segmentation, while helpful, falls short in the face of the heterogeneous nature of IoT devices. Many IoT devices operate on legacy protocols and lack robust security features. Simply placing them on a separate network segment isn’t sufficient. The solution lies in micro-segmentation. This advanced technique divides the network into incredibly granular segments, isolating individual devices or groups of devices with similar security profiles and functionalities.
Imagine a smart factory: robots, sensors, and PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) can each reside in their own micro-segment, limiting the impact of a breach. If a sensor is compromised, the attacker’s lateral movement is restricted, preventing access to critical control systems. Implementing micro-segmentation requires sophisticated network management tools and a clear understanding of device interdependencies. Consider using network virtualization technologies like Software-Defined Networking (SDN) to dynamically manage these micro-segments and adapt to changing network configurations.
2. Zero Trust Architecture: Never Trust, Always Verify
The "trust but verify" approach is obsolete in the IoT landscape. A Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) assumes no implicit trust, verifying every device and user attempting access to the network, regardless of location. For IoT devices, this means implementing strong authentication mechanisms like digital certificates, hardware security modules (HSMs), and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Furthermore, ZTA incorporates continuous monitoring and threat detection. Anomaly detection systems can identify unusual device behavior, flagging potential compromises. Microsegmentation, discussed above, is a key component of ZTA, restricting device access based on verified identity and context. Adopting a ZTA requires a cultural shift, demanding a move away from broad network access towards granular, permission-based controls.
3. Firmware Security: The Often-Forgotten Foundation
IoT devices are often shipped with outdated or vulnerable firmware. This is a major security weakness, providing attackers with easy entry points. A robust firmware management strategy is critical. This includes:
- Regular firmware updates: Develop a rigorous patching schedule to address known vulnerabilities promptly. Automate the update process as much as possible to minimize manual intervention and potential errors.
- Firmware signing and verification: Ensure that only authorized and verified firmware is installed on devices. Digital signatures provide integrity and authenticity checks.
- Secure boot processes: Implement secure boot mechanisms to prevent unauthorized firmware execution. This ensures that only legitimate firmware is loaded during device startup.
- Firmware analysis: Regularly analyze the firmware of your IoT devices for vulnerabilities using static and dynamic analysis techniques. This proactive approach allows you to identify and address potential issues before they can be exploited.

4. Data Encryption: Securing Data at Rest and in Transit
Protecting data from unauthorized access is paramount. Encryption is essential for both data at rest (stored on the device) and data in transit (communicating between devices and the network). Employ strong encryption algorithms like AES-256 for both scenarios. Consider using hardware-based encryption for enhanced security.
Furthermore, implement secure data disposal mechanisms to ensure that data is permanently erased when devices are decommissioned or replaced. This prevents data leakage even after the device is no longer in use. Data encryption is not a one-time task; it requires ongoing management and monitoring to ensure effectiveness.
5. Behavioral Analytics and Anomaly Detection: Proactive Threat Hunting
Traditional signature-based intrusion detection systems (IDS) are insufficient for detecting sophisticated IoT attacks. Behavioral analytics and anomaly detection are far more effective. These systems learn the normal behavior of each device and identify deviations that could indicate malicious activity.
Anomaly detection systems can flag unusual communication patterns, unexpected resource consumption, or other anomalies that might escape the notice of traditional security tools. These systems require extensive data collection and analysis capabilities, often leveraging machine learning algorithms to identify subtle patterns indicative of compromise.
6. Device Inventory and Management: Knowing What You Have
A comprehensive inventory of all IoT devices within your network is crucial. This inventory should include device details like manufacturer, model, firmware version, location, and network connectivity. This information is essential for effective security management, allowing you to identify vulnerable devices and prioritize patching efforts.
Employ a Device Management System (DMS) to automate the inventory process and track device status. The DMS should integrate with your security information and event management (SIEM) system to provide a holistic view of your IoT security posture. Regularly audit your device inventory to ensure accuracy and identify any unauthorized devices.
7. Security Awareness Training: The Human Element
IoT security isn’t solely a technological problem; it’s also a human one. Employees need to be aware of the risks associated with IoT devices and how to mitigate them. Security awareness training should cover topics like phishing attacks targeting IoT devices, the importance of strong passwords, and the risks of connecting unauthorized devices to the network.
This training should be tailored to the specific roles and responsibilities of your employees. Regular refresher training is essential to keep employees updated on the latest threats and best practices. Remember, human error remains a major vulnerability in any security system.
8. Incident Response Planning: Preparing for the Inevitable
Despite your best efforts, security breaches can occur. A well-defined incident response plan is crucial for minimizing the impact of a compromise. This plan should outline the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident, including:
- Detection and identification: Establish procedures for detecting and identifying security incidents.
- Containment: Implement measures to contain the incident and prevent further damage.
- Eradication: Remove the threat and restore the affected systems.
- Recovery: Restore systems to their normal operating state.
- Post-incident activity: Analyze the incident to identify vulnerabilities and improve security measures.
Regularly test and update your incident response plan to ensure its effectiveness. Simulate security incidents to train your team and identify weaknesses in your procedures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the biggest IoT security threats in 2025?
A: The biggest threats will include sophisticated attacks targeting firmware vulnerabilities, lateral movement within the network exploiting poorly segmented systems, data breaches resulting from insufficient encryption, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks targeting critical infrastructure. The human element, through phishing and social engineering, will also remain a significant threat vector.
Q: How can I choose secure IoT devices?
A: Look for devices with strong security features like secure boot, firmware updates, encryption, and robust authentication mechanisms. Choose reputable vendors with a proven track record of security. Consider devices with built-in security certifications, such as those from NIST or other relevant organizations.
Q: Is it necessary to replace all my existing IoT devices?
A: Not necessarily. Many legacy devices can be secured through firmware updates, security patching, and network segmentation. However, if a device is too old or lacks the necessary security features, replacement may be necessary.
Q: What is the role of AI and machine learning in IoT security?
A: AI and machine learning are increasingly important for anomaly detection, threat hunting, and predictive security. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify subtle patterns indicative of malicious activity that might be missed by traditional security tools.
Q: How much will securing IoT devices cost?
A: The cost varies significantly depending on the size and complexity of your IoT ecosystem, the level of security required, and the technologies implemented. However, the cost of not securing your IoT devices is likely to be far greater, potentially leading to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities.
Q: How can I stay updated on the latest IoT security threats and best practices?
A: Stay informed by following industry news, attending security conferences, and subscribing to security newsletters and blogs. Engage with security professionals and participate in online communities focused on IoT security.
Securing your business’s IoT ecosystem in 2025 requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing technology, processes, and people. By implementing the strategies outlined in this article and staying abreast of emerging threats, you can significantly reduce your risk and protect your valuable business assets.
Source URL: [Insert a relevant URL from a reputable cybersecurity source, such as NIST, SANS Institute, or a similar organization. For example: https://www.nist.gov/cybersecurity]
Closure
Thank you for reading! Stay with us for more insights on Securing IoT devices in business networks 2025.
Make sure to follow us for more exciting news and reviews.
Feel free to share your experience with Securing IoT devices in business networks 2025 in the comment section.
Stay informed with our next updates on Securing IoT devices in business networks 2025 and other exciting topics.
