Role of ethical hacking in securing enterprise data
Related Articles
- How Machine Learning Is Transforming Business Data Protection
- “best Practices For Securing Business Data Backups”
- “cybersecurity Risks Associated With AI-powered Tools”
- “how To Prevent Double-extortion Ransomware Attacks”
- “cybersecurity Measures For Protecting Business APIs”
Introduction
In this article, we dive into Role of ethical hacking in securing enterprise data, giving you a full overview of what’s to come
Protecting this invaluable asset requires a multi-layered defense strategy, and increasingly, ethical hacking is emerging as a crucial component. While the term "hacking" often evokes images of malicious actors, ethical hacking, also known as penetration testing, is a proactive and legally sanctioned approach to identifying vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them. This article delves into the often-overlooked secrets and strategies employed by ethical hackers to fortify enterprise data security, offering valuable insights for organizations seeking to bolster their defenses.

1. Beyond the Firewall: Unveiling Hidden Vulnerabilities
Traditional security measures like firewalls and antivirus software form the first line of defense, but they are not foolproof. Ethical hackers go beyond these basic protections, employing a diverse arsenal of techniques to uncover hidden vulnerabilities. This involves actively attempting to breach the system, simulating real-world attacks to identify weaknesses in network infrastructure, application security, and even human factors. These "secret" techniques often include:
- Social Engineering Simulations: These aren’t just about phishing emails. Ethical hackers might attempt to manipulate employees through phone calls, in-person interactions, or even cleverly crafted physical lures to assess the human element of security – often the weakest link. The goal isn’t to trick employees, but to identify vulnerabilities in training, awareness, and procedures.
- Network Mapping and Enumeration: Ethical hackers use specialized tools to map the entire network infrastructure, identifying all devices, services, and protocols. This provides a comprehensive overview of the attack surface, pinpointing potential entry points for malicious actors. Techniques like port scanning, service discovery, and vulnerability scanning are crucial here.
- Exploit Development and Testing: Once vulnerabilities are identified, ethical hackers may develop and test exploits – carefully crafted pieces of code designed to exploit specific weaknesses. This allows them to assess the potential impact of a successful attack and determine the severity of the vulnerability. This process is meticulously documented and controlled to prevent accidental damage.
- Wireless Security Assessments: With the prevalence of Wi-Fi networks, wireless security is paramount. Ethical hackers conduct assessments to identify vulnerabilities in wireless access points, encryption protocols, and network configurations, ensuring that wireless connections are secure. This includes testing for weak passwords, rogue access points, and vulnerabilities in wireless protocols.
- Database Security Audits: Databases are often the target of data breaches. Ethical hackers assess database security by testing for vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, insecure configurations, and weak access controls. This involves analyzing database queries, examining user permissions, and identifying potential points of compromise.
2. The Art of Deception: Mimicking Real-World Attacks
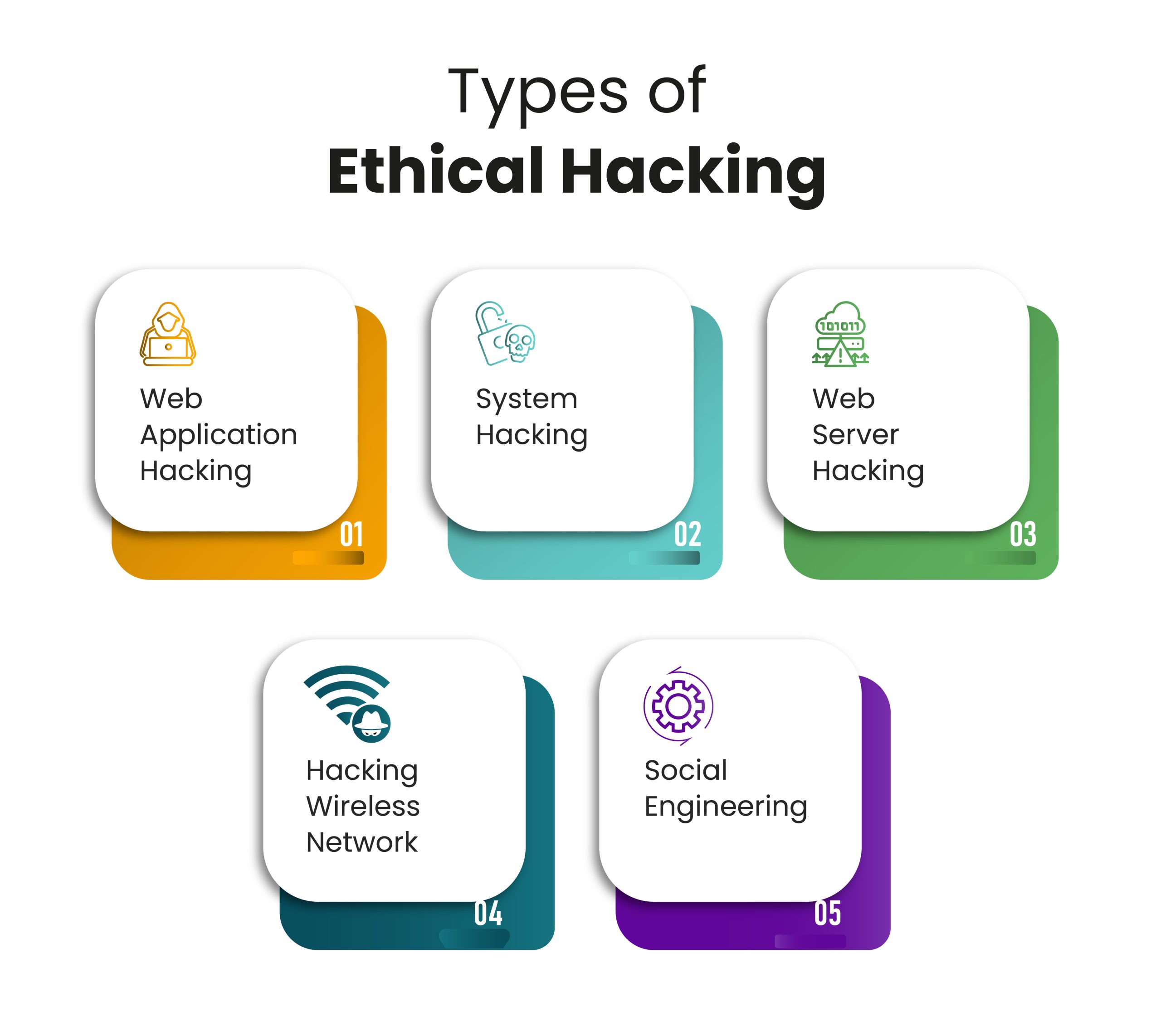
A key aspect of ethical hacking is its ability to simulate real-world attacks. This means going beyond simple vulnerability scans and actively attempting to compromise systems, mirroring the tactics of malicious hackers. This "secret" lies in understanding the attacker’s mindset and employing similar techniques, but with the crucial difference of obtaining explicit permission and working to improve security.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APT) Simulations: APTs involve sophisticated, long-term attacks designed to remain undetected for extended periods. Ethical hackers can simulate these attacks to test the resilience of the organization’s security infrastructure against prolonged and targeted attacks.
- Zero-Day Exploit Simulations: These simulations focus on exploiting newly discovered vulnerabilities before patches are available. This requires a deep understanding of software vulnerabilities and the ability to quickly develop and deploy exploits, mirroring the actions of advanced threat actors.
- Insider Threat Simulations: Ethical hackers can simulate insider threats by creating scenarios where employees with privileged access attempt to compromise systems or data. This helps identify weaknesses in access control, monitoring, and employee behavior policies.
3. Beyond Technical Skills: The Human Factor
While technical expertise is crucial, ethical hacking also relies heavily on understanding the human element. This involves analyzing employee behavior, identifying social engineering vulnerabilities, and assessing the overall security awareness within the organization.
- Security Awareness Training Effectiveness Testing: Ethical hackers can evaluate the effectiveness of security awareness training programs by conducting phishing campaigns and other social engineering tests. This helps identify areas for improvement in employee training and awareness.
- Vulnerability Reporting and Remediation Processes: A crucial aspect of ethical hacking is the reporting and remediation process. Ethical hackers meticulously document their findings, providing detailed reports that include vulnerability descriptions, severity levels, and recommended remediation steps. They work closely with the organization to ensure that vulnerabilities are addressed promptly and effectively. This involves testing the effectiveness of the organization’s incident response plan.
4. The Power of Collaboration: A Holistic Approach
Ethical hacking is not an isolated activity. It requires close collaboration between ethical hackers, security teams, and other stakeholders within the organization. This collaborative approach ensures that vulnerabilities are identified and addressed effectively, leading to a more robust and resilient security posture.
- Integrating Ethical Hacking into the SDLC: Integrating ethical hacking into the software development lifecycle (SDLC) allows for the identification and remediation of vulnerabilities early in the development process, reducing the risk of costly security breaches later on. This involves conducting security assessments at various stages of the development process.
- Red Teaming and Blue Teaming Exercises: Red teaming involves simulating real-world attacks against the organization’s systems, while blue teaming focuses on defending against these attacks. These exercises provide valuable insights into the organization’s security capabilities and identify areas for improvement.
5. Staying Ahead of the Curve: Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
The landscape of cyber threats is constantly evolving. Ethical hackers must continuously update their skills and knowledge to stay ahead of the curve. This involves staying informed about the latest vulnerabilities, attack techniques, and security technologies.
- Continuous Vulnerability Scanning: Regular vulnerability scanning and penetration testing are crucial for identifying and addressing emerging threats. This involves using automated tools and manual techniques to identify vulnerabilities in systems and applications.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Integrating threat intelligence into the ethical hacking process allows for a more proactive and targeted approach to security assessments. This involves leveraging threat intelligence feeds to identify emerging threats and tailor assessments to address specific risks.
6. Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Measuring the success of ethical hacking initiatives is crucial. This involves defining key performance indicators (KPIs) that track the effectiveness of the program. These KPIs might include:
- Number of vulnerabilities identified and remediated.
- Time taken to remediate vulnerabilities.
- Reduction in security incidents.
- Improved security awareness among employees.
- Cost savings from preventing security breaches.
7. Legal and Ethical Considerations: Navigating the Grey Areas
Ethical hacking operates within a strict legal and ethical framework. It’s crucial to obtain explicit written permission before conducting any penetration testing activities. This permission should clearly define the scope of the assessment, the permitted techniques, and the responsibilities of both the ethical hacker and the organization. Transparency and clear communication are paramount.
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between ethical hacking and malicious hacking?
A: Ethical hacking is conducted with explicit permission from the organization and aims to improve security. Malicious hacking is illegal and aims to cause damage or steal data.
Q: How much does ethical hacking cost?
A: The cost of ethical hacking services varies depending on the scope of the assessment, the size of the organization, and the expertise required.
Q: How often should an organization conduct penetration testing?
A: The frequency of penetration testing depends on several factors, including the organization’s risk profile, industry regulations, and the complexity of its IT infrastructure. However, annual penetration testing is often recommended as a minimum.
Q: What are the qualifications of a good ethical hacker?
A: A good ethical hacker possesses a strong understanding of networking, operating systems, security protocols, and programming. They also possess strong analytical and problem-solving skills, as well as excellent communication and reporting abilities. Relevant certifications like CEH, OSCP, and CISSP are often sought after.
In conclusion, ethical hacking is not merely a technical exercise; it’s a strategic approach to securing enterprise data that combines technical expertise, human psychology, and a collaborative spirit. By embracing these "secret" tips and tricks, organizations can significantly strengthen their defenses and protect their valuable assets from the ever-evolving threat landscape. The continuous adaptation and integration of ethical hacking into a broader security strategy are essential for long-term success in the ongoing battle for data security.
Source URL: [Insert a relevant URL from a reputable cybersecurity resource here, e.g., a NIST publication or SANS Institute article]
Closure
Thank you for reading! Stay with us for more insights on Role of ethical hacking in securing enterprise data.
Don’t forget to check back for the latest news and updates on Role of ethical hacking in securing enterprise data!
Feel free to share your experience with Role of ethical hacking in securing enterprise data in the comment section.
Stay informed with our next updates on Role of ethical hacking in securing enterprise data and other exciting topics.
