“role of endpoint detection and response (EDR) in business security”
Related Articles
- “how To Secure IoT Devices In Corporate Networks”
- “ransomware Recovery Strategies For Enterprises In 2025”
- “challenges Of Securing Data In Hybrid Cloud Environments”
- “AI-driven Threat Detection Tools For Businesses”
- “how To Implement Post-quantum Encryption Technologies”
Introduction
Discover everything you need to know about “role of endpoint detection and response (EDR) in business security”
From sophisticated ransomware campaigns to subtle data breaches, the potential for damage is immense. While traditional security measures like firewalls and antivirus software remain crucial, they are often insufficient to combat the agility and sophistication of modern threats. This is where Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) steps in, acting as an unsung hero in the fight for business security. This article delves into the often-overlooked aspects of EDR, revealing big secret tips and tricks to maximize its effectiveness and solidify your organization’s defenses.
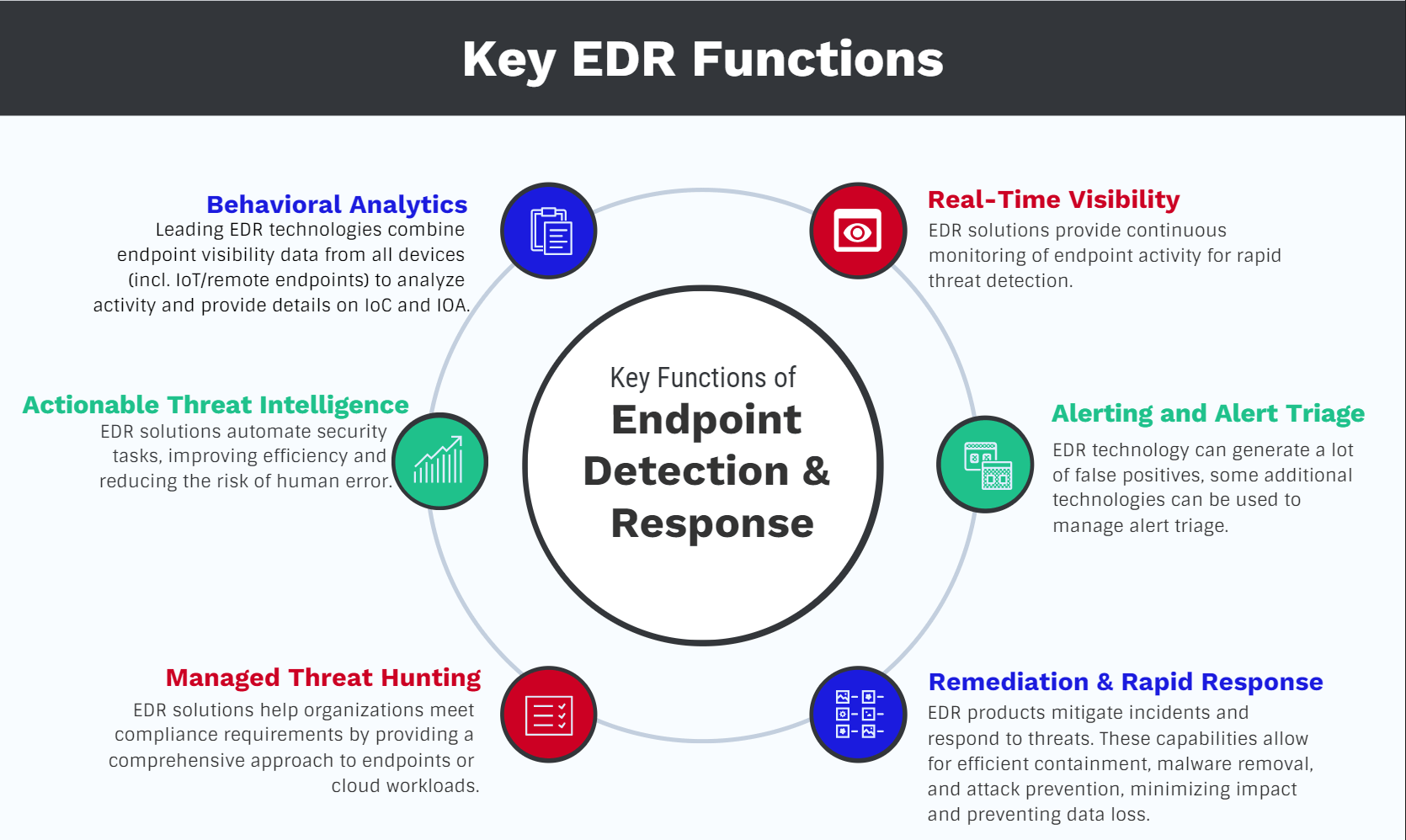
1. Beyond Antivirus: EDR’s Multi-Layered Approach to Threat Hunting
EDR transcends the limitations of traditional antivirus solutions. Antivirus primarily relies on signature-based detection, identifying known threats based on pre-defined patterns. This approach is inherently reactive, failing to detect zero-day exploits and novel malware variants. EDR, on the other hand, employs a multi-layered approach, combining several advanced techniques:
- Behavioral Analysis: EDR continuously monitors endpoint activity, analyzing processes, network connections, and file system changes to detect anomalies indicative of malicious behavior. This allows it to identify threats even without prior knowledge of their signatures.
- Heuristic Analysis: This technique uses algorithms to identify suspicious patterns and behaviors, flagging potentially malicious activities based on their characteristics, even if they are not yet recognized by traditional methods.
- Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI): Advanced EDR solutions leverage ML and AI to improve threat detection accuracy. These technologies analyze vast amounts of data to identify subtle patterns and anomalies that might escape human detection. They continuously learn and adapt, improving their ability to detect new and evolving threats.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: EDR systems often integrate with threat intelligence feeds, providing real-time updates on the latest threats and vulnerabilities. This allows them to proactively identify and mitigate emerging risks.
The combination of these techniques provides a proactive and adaptive defense, significantly improving the detection rate of both known and unknown threats. This proactive approach is a key differentiator from traditional antivirus, allowing businesses to stay ahead of the curve.
2. Unlocking the Power of EDR: Data Correlation and Contextual Analysis
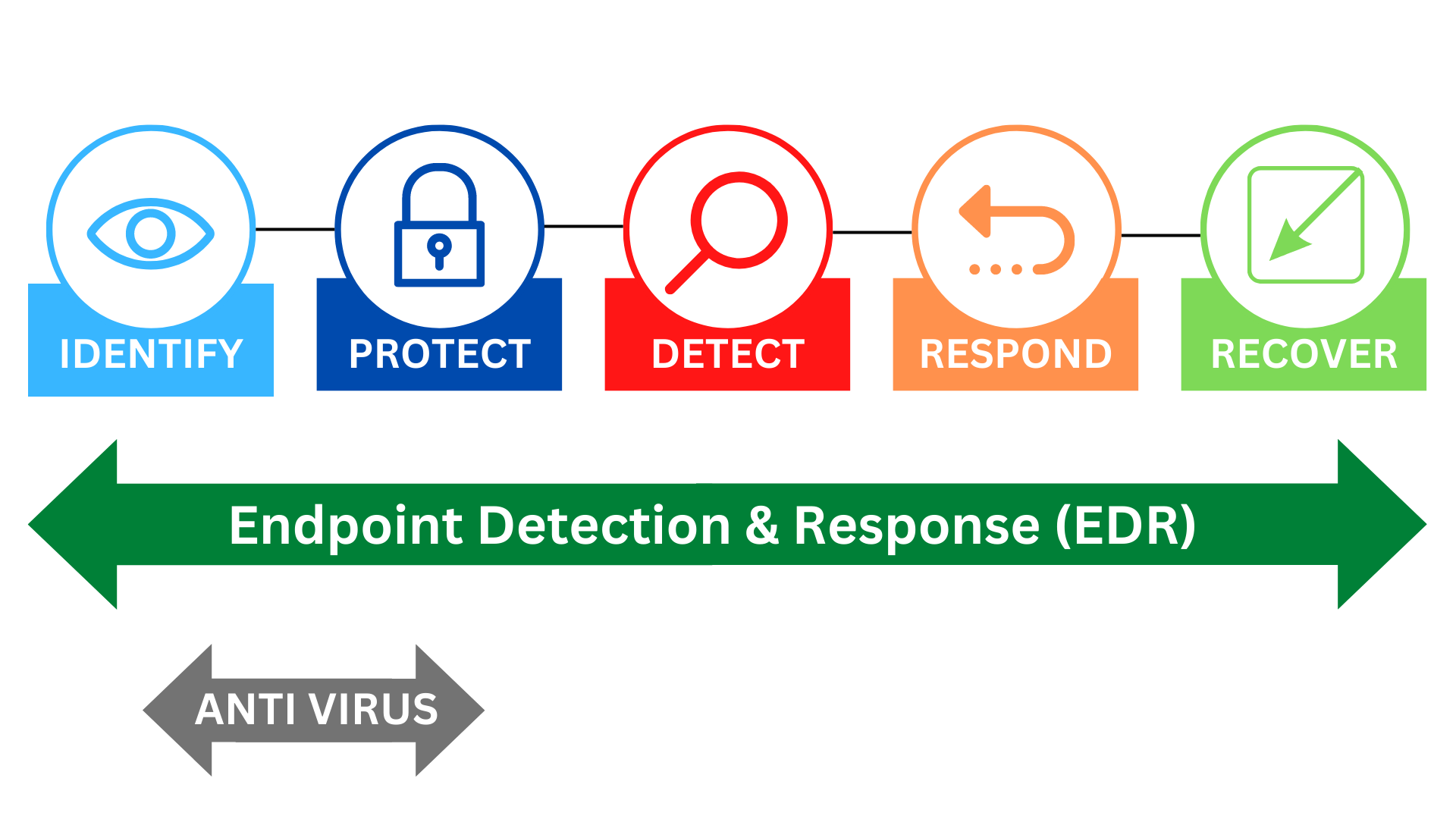
One of the biggest secrets to maximizing EDR’s effectiveness lies in understanding and leveraging its data correlation and contextual analysis capabilities. EDR solutions collect vast amounts of data from endpoints, creating a comprehensive picture of their activity. The ability to correlate this data across different endpoints and systems is critical for effective threat hunting.
For example, detecting a single suspicious process on one machine might not be alarming. However, if several machines exhibit similar suspicious activity within a short time frame, it could indicate a coordinated attack. EDR’s ability to correlate data across endpoints allows security teams to identify such patterns and respond swiftly.
Contextual analysis further enhances this capability. By considering factors such as user location, time of day, and application usage, EDR can determine whether an activity is truly suspicious or simply a legitimate operation. This reduces the number of false positives, allowing security teams to focus on genuine threats.
This ability to connect the dots and understand the "why" behind suspicious activity is a significant advantage, turning raw data into actionable intelligence.
3. Beyond Detection: The Crucial Role of Response in EDR
The "Response" in EDR is just as critical as the "Detection." Effective response capabilities are essential for minimizing the impact of a successful attack. EDR solutions offer a range of response options, including:
- Automated Remediation: Many EDR systems can automatically contain and neutralize threats, minimizing the time it takes to respond to an incident. This might involve isolating infected endpoints, terminating malicious processes, or quarantining infected files.
- Remote Investigation: Security teams can remotely investigate infected endpoints, analyzing logs, memory dumps, and other data to understand the nature of the attack and its impact.
- Incident Response Orchestration: EDR can integrate with other security tools, enabling automated incident response workflows. This allows security teams to streamline their response processes and improve their efficiency.
- Rollback Capabilities: Some advanced EDR solutions offer rollback capabilities, allowing them to revert infected systems to a previous, clean state. This can be particularly effective in mitigating the impact of ransomware attacks.
The ability to rapidly respond to threats is crucial in minimizing damage and downtime. The integrated response capabilities of EDR significantly improve the speed and efficiency of incident response, a vital component of a strong security posture.
4. Choosing the Right EDR Solution: A Deep Dive into Vendor Selection
Selecting the right EDR solution is crucial for maximizing its effectiveness. The market is saturated with various vendors, each offering different features and capabilities. Careful consideration of several factors is essential:
- Integration with Existing Security Infrastructure: The chosen EDR solution should seamlessly integrate with your existing security tools, such as SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems, SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) platforms, and other security controls. This ensures a unified and cohesive security posture.
- Scalability and Performance: The solution should be scalable to accommodate your organization’s growth and evolving needs. It should also perform efficiently without impacting the performance of your endpoints.
- Ease of Use and Management: The solution should be easy to use and manage, even for security teams with limited resources. A user-friendly interface and comprehensive documentation are essential.
- Threat Intelligence Coverage: The solution should leverage high-quality threat intelligence feeds to stay ahead of emerging threats.
- Deployment Flexibility: The solution should offer flexible deployment options, such as cloud-based, on-premises, or hybrid deployments, to accommodate your organization’s specific infrastructure.
Thorough research and vendor comparison are essential to ensure that you select a solution that meets your organization’s specific needs and budget.
5. EDR Deployment Best Practices: Maximizing Effectiveness
Effective EDR deployment requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices:
- Comprehensive Endpoint Coverage: Ensure that all critical endpoints, including servers, workstations, and mobile devices, are covered by the EDR solution.
- Regular Updates and Patching: Keep the EDR solution and its components updated with the latest patches and signatures to ensure optimal protection.
- Proper Configuration: Configure the EDR solution correctly to optimize its performance and effectiveness. This includes setting appropriate alert thresholds and tuning detection rules.
- Security Awareness Training: Educate employees about the importance of cybersecurity and train them to recognize and report suspicious activities.
- Regular Testing and Validation: Regularly test the EDR solution to ensure that it is functioning correctly and effectively detecting and responding to threats. Conduct penetration testing and simulated attacks to identify weaknesses.
Following these best practices will significantly enhance the effectiveness of your EDR deployment.
6. The Human Element: EDR and Your Security Team
While EDR provides powerful automated capabilities, the human element remains crucial. Security analysts play a vital role in interpreting alerts, investigating incidents, and responding to threats. Effective utilization of EDR requires skilled analysts capable of:
- Alert Triage and Prioritization: Analysts must be able to prioritize alerts based on their severity and potential impact, focusing their attention on the most critical threats.
- Threat Hunting and Investigation: Analysts should actively hunt for threats, using EDR’s capabilities to investigate suspicious activity and identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Incident Response and Remediation: Analysts are responsible for responding to security incidents, containing threats, and remediating vulnerabilities.
- Continuous Improvement: Analysts should continuously evaluate the effectiveness of the EDR solution and make adjustments as needed.
Investing in training and development for your security team is essential for maximizing the value of your EDR investment.
7. The Future of EDR: Emerging Trends and Technologies
The field of EDR is constantly evolving, with new technologies and approaches emerging regularly. Some key trends include:
- Extended Detection and Response (XDR): XDR expands EDR’s capabilities by integrating data from multiple security sources, such as network security, cloud security, and email security. This provides a more holistic view of the security landscape and improves threat detection and response.
- AI-Powered Threat Hunting: AI and ML are playing an increasingly important role in threat hunting, enabling security analysts to identify subtle and complex threats that might escape human detection.
- Automation and Orchestration: Automation is becoming increasingly important in EDR, enabling faster and more efficient threat response. SOAR platforms are playing a key role in automating incident response workflows.
- Focus on Prevention: While detection and response remain crucial, there is a growing focus on preventing attacks in the first place. EDR solutions are increasingly incorporating preventative measures, such as vulnerability management and security awareness training.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the difference between EDR and Antivirus?
A1: Antivirus primarily relies on signature-based detection, identifying known threats. EDR goes beyond this, using behavioral analysis, heuristic analysis, machine learning, and threat intelligence to detect both known and unknown threats. EDR also provides advanced response capabilities, allowing for automated remediation and incident response orchestration.
Q2: How much does EDR cost?
A2: The cost of EDR varies depending on the vendor, the number of endpoints, and the features included. Pricing models can range from per-endpoint licensing to subscription-based services.
Q3: How long does it take to implement EDR?
A3: Implementation time varies depending on the complexity of your environment and the chosen solution. However, many solutions can be deployed relatively quickly, with some offering streamlined deployment processes.
Q4: Does EDR impact endpoint performance?
A4: While EDR does consume some system resources, modern solutions are designed to minimize performance impact. Careful configuration and optimization can further mitigate any performance issues.
Q5: How can I measure the effectiveness of my EDR solution?
A5: Measure effectiveness by tracking key metrics like the number of threats detected, the time to detect and respond to threats, the number of false positives, and the overall reduction in security incidents. Regular testing and penetration testing are also crucial.
Q6: What are the biggest challenges in using EDR?
A6: Challenges include managing alert fatigue, ensuring proper configuration and tuning, integrating EDR with other security tools, and having skilled personnel to manage and analyze the data.
This comprehensive exploration of EDR’s role in business security provides a strong foundation for understanding its capabilities and maximizing its potential. By embracing the secrets and best practices outlined here, businesses can significantly enhance their security posture and protect themselves against the ever-evolving threat landscape. Remember, continuous learning and adaptation are key to staying ahead in the ongoing battle for cyber security.
Source URL: [Insert a relevant URL from a reputable cybersecurity source, such as SANS Institute, NIST, or a major security vendor’s website.] (e.g., https://www.sans.org/reading-room/whitepapers/detection/endpoint-detection-response-edr-37217)
Closure
We hope this article has helped you understand everything about “role of endpoint detection and response (EDR) in business security”. Stay tuned for more updates!
Don’t forget to check back for the latest news and updates on “role of endpoint detection and response (EDR) in business security”!
Feel free to share your experience with “role of endpoint detection and response (EDR) in business security” in the comment section.
Keep visiting our website for the latest trends and reviews.
