“impact of quantum computing on business data encryption”
Related Articles
- “best Practices For Implementing Zero Trust Architecture In Business”
- “how To Protect Sensitive Business Data From Ransomware”
- “top Cybersecurity Threats To Small Businesses In 2025”
- “how AI Is Reshaping Data Security Strategies In 2025”
Introduction
Join us as we explore “impact of quantum computing on business data encryption”, packed with exciting updates
While it promises unprecedented computational power with applications across various sectors, it also poses a significant threat to the security of current data encryption methods. Understanding this threat and proactively adapting security strategies is no longer a luxury, but a necessity for survival in the digital age. This article delves into the impact of quantum computing on business data encryption, revealing both the looming danger and the emerging strategies to mitigate it. We will explore "big secret" tips and tricks – strategies that are not widely known but are crucial for future-proofing your data.

I. The Looming Quantum Threat: An In-Depth Exploration
Classical computers store information as bits, representing either 0 or 1. Quantum computers, however, leverage the principles of quantum mechanics to utilize qubits. Qubits can exist in a superposition, representing both 0 and 1 simultaneously. This, along with other quantum phenomena like entanglement, allows quantum computers to perform calculations exponentially faster than classical computers for specific types of problems. This exponential speedup is particularly alarming for cryptography.
Many widely used encryption algorithms, such as RSA and ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography), rely on the computational difficulty of factoring large numbers or solving the discrete logarithm problem for classical computers. These problems are computationally intractable for classical machines, ensuring the security of encrypted data. However, Shor’s algorithm, a quantum algorithm developed by Peter Shor in 1994, can efficiently solve these problems on a sufficiently powerful quantum computer. This means that a sufficiently advanced quantum computer could break widely used encryption methods in a fraction of the time it would take a classical computer, rendering current security measures obsolete.
The implications for businesses are staggering. Confidential customer data, intellectual property, financial transactions, and sensitive internal communications could all be vulnerable to attack. A successful breach could lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, legal repercussions, and even national security risks depending on the nature of the data. The timeline for this threat is uncertain, but experts agree that the risk is real and growing rapidly. The development of fault-tolerant quantum computers is progressing at a faster pace than many anticipated, making proactive measures essential.
II. Progression of Tips and Tricks: Adapting to the Quantum Threat
The response to the quantum threat is evolving, moving beyond simple awareness to proactive strategic planning and implementation. This progression can be categorized into several key phases:
A. Awareness and Assessment: The first step involves understanding the potential impact of quantum computing on your specific business. This includes identifying critical data assets, assessing the risk level based on the sensitivity of the data and the potential consequences of a breach, and determining the likelihood of becoming a target.
B. Inventory and Prioritization: Once the risk is assessed, businesses need to inventory their current encryption methods and prioritize the data that needs the strongest protection. This includes identifying systems and applications using vulnerable algorithms and developing a roadmap for migration.
C. Migration to Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC): This is the most crucial step. PQC refers to cryptographic algorithms that are believed to be resistant to attacks from both classical and quantum computers. Several PQC candidates are currently under evaluation by standardization bodies like NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology). Businesses need to identify suitable PQC algorithms based on their specific needs and migrate their systems to use these algorithms. This is a complex and time-consuming process requiring expertise in cryptography and secure coding practices.
D. Quantum-Resistant Infrastructure: Beyond algorithm changes, businesses must consider the broader infrastructure implications. This includes secure key management systems, robust hardware security modules (HSMs), and secure software development lifecycle (SDLC) practices to prevent vulnerabilities that could weaken even the strongest PQC algorithms.
E. Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation: The quantum computing landscape is constantly evolving. Businesses must implement continuous monitoring and threat intelligence gathering to stay ahead of emerging threats and adapt their security strategies accordingly. This includes staying updated on the latest developments in PQC research and regularly reviewing and updating their security protocols.
III. Big Secret Tips and Tricks: Beyond the Obvious
While the progression outlined above is critical, several "big secret" tips and tricks can significantly enhance your organization’s quantum-resistance:
1. Focus on Hybrid Approaches: Don’t solely rely on a single PQC algorithm. Employ a layered security approach combining different PQC algorithms and classical methods to create a more resilient system. This redundancy mitigates the risk of a single point of failure.
2. Embrace Homomorphic Encryption: This advanced encryption technique allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without decryption. This is particularly valuable for cloud computing and data analysis where data needs to be processed without compromising its confidentiality. While computationally intensive, its potential for protecting sensitive data in quantum-resistant ways is immense.
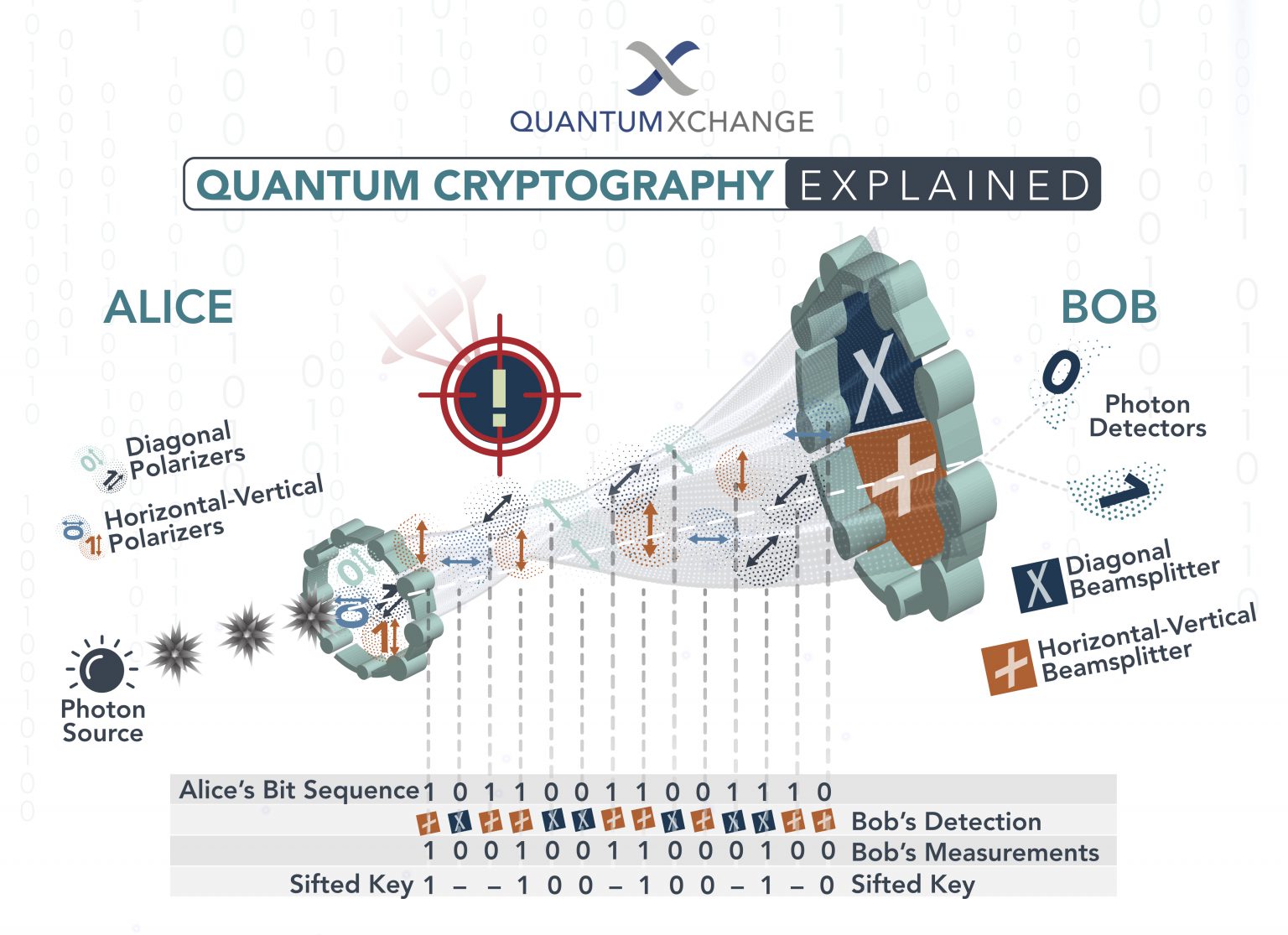
3. Invest in Quantum Key Distribution (QKD): QKD utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to establish a secure communication channel for exchanging cryptographic keys. This technology offers a fundamentally secure way to distribute keys, eliminating the risk of key compromise through classical means. While still in its early stages of development, QKD represents a promising long-term solution.
4. Prioritize Software Supply Chain Security: Many security breaches originate from vulnerabilities in third-party software. Businesses need to rigorously vet their software suppliers, implement secure software development practices, and regularly audit their software supply chain to mitigate the risk of introducing quantum-vulnerable components.
5. Develop a Quantum-Ready Workforce: The transition to post-quantum cryptography requires expertise in quantum computing, cryptography, and secure coding practices. Investing in training and development programs to build a quantum-ready workforce is crucial for successful implementation and long-term security.
6. Engage with the Quantum Community: Actively participate in industry forums, research collaborations, and standardization efforts to stay informed about the latest developments in quantum computing and PQC. This proactive engagement ensures you’re not caught off guard by emerging threats.
7. Consider Quantum-Resistant Hardware: Specific hardware architectures might offer inherent resistance to quantum attacks. Exploring and adopting such hardware solutions, when available, can enhance overall security.
IV. Conclusion: Proactive Security is Paramount
The threat posed by quantum computing to business data encryption is undeniable. Ignoring this threat is not an option. By proactively implementing the strategies outlined above, including the "big secret" tips and tricks, businesses can significantly enhance their resilience against future quantum attacks. This requires a multifaceted approach encompassing algorithm migration, infrastructure upgrades, workforce development, and continuous monitoring. The transition to a quantum-resistant future will be a journey, not a destination, requiring ongoing vigilance and adaptation. The sooner businesses begin this journey, the better prepared they will be to protect their valuable data in the quantum era.
V. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: When will quantum computers be able to break current encryption?
A: The exact timeline is uncertain. While progress is rapid, building fault-tolerant quantum computers capable of breaking widely used encryption is a significant engineering challenge. Estimates range from several years to a couple of decades. However, the potential for a sudden breakthrough cannot be ruled out.
Q: Is post-quantum cryptography a guaranteed solution?
A: While PQC algorithms are designed to resist attacks from both classical and quantum computers, there’s no absolute guarantee of security. Future breakthroughs in quantum computing could potentially compromise even PQC algorithms. Therefore, a layered approach and continuous monitoring are crucial.
Q: How much will the transition to PQC cost?
A: The cost varies significantly depending on the size and complexity of a business’s IT infrastructure. It involves not only the cost of algorithm migration but also potential infrastructure upgrades, training, and consulting fees. Early adoption might be more cost-effective in the long run compared to reacting to a breach.
Q: What role does government regulation play?
A: Governments worldwide are actively involved in developing standards, promoting research, and potentially mandating the adoption of PQC. Staying informed about relevant regulations and industry best practices is essential.
Source URL: [Insert a relevant URL here, for example, a NIST website regarding post-quantum cryptography or a reputable cybersecurity firm’s report on quantum computing threats.] (Example: https://csrc.nist.gov/Projects/post-quantum-cryptography)
Closure
We hope this article has helped you understand everything about “impact of quantum computing on business data encryption”. Stay tuned for more updates!
Make sure to follow us for more exciting news and reviews.
We’d love to hear your thoughts about “impact of quantum computing on business data encryption”—leave your comments below!
Keep visiting our website for the latest trends and reviews.