“impact of GDPR and CCPA on data security practices”
Related Articles
- “how To Create A Cybersecurity Response Plan For SMBs”
- “emerging Cybersecurity Solutions For Protecting Intellectual Property”
- “securing Financial Transactions With Post-quantum Cryptography”
- “managing Third-party Risk In Data Security Strategies”
- Businesses Can Face Numerous Other Legal Challenges, Including:
Introduction
Welcome to our in-depth look at “impact of GDPR and CCPA on data security practices”
While often perceived as purely legal frameworks, their impact extends far beyond compliance, fundamentally reshaping data security practices worldwide. This article delves into the "big secret" – the often-overlooked nuances and strategic advantages – of adapting to these regulations, offering valuable insights for businesses of all sizes.
1. Beyond Compliance: Building a Culture of Data Security
The most significant impact of GDPR and CCPA isn’t just about ticking boxes on a checklist; it’s about fostering a culture of data security. Simply implementing technical controls is insufficient. These regulations demand a holistic approach, integrating data protection into every aspect of the organization, from product design to employee training. This cultural shift involves:
-
Data Minimization by Design: Instead of collecting vast amounts of data upfront, organizations must proactively identify the minimum necessary data for specific purposes. This approach reduces the attack surface, minimizing the potential damage from a breach. It also necessitates a reassessment of existing data collection practices, often revealing unnecessary or outdated data points.
-
Privacy by Design (PbD): PbD integrates data protection into the entire lifecycle of a product or service, from conception to disposal. This proactive approach ensures data protection is not an afterthought but a core element of the design process. It involves careful consideration of data flow, access controls, and security mechanisms from the outset.

Employee Training and Awareness: Employees are often the weakest link in data security. Comprehensive training programs that go beyond basic awareness and address specific GDPR and CCPA requirements are crucial. This includes training on data handling procedures, incident response protocols, and the consequences of non-compliance. Regular refresher courses and simulated phishing exercises should be part of the strategy.
2. Data Mapping: The Foundation of Effective Data Governance
Effective data governance is the cornerstone of GDPR and CCPA compliance. This begins with comprehensive data mapping, a process of identifying, classifying, and documenting all personal data an organization processes. This seemingly simple step often reveals hidden vulnerabilities and unexpected data flows.
-
Identifying Data Types and Sources: This involves meticulously cataloging all personal data, including its format, location, and purpose. This goes beyond obvious data like names and addresses to encompass less obvious information such as IP addresses, cookies, and device identifiers.
-
Determining Data Flows: Mapping the journey of data from its point of origin to its final destination is crucial. This helps identify potential risks and vulnerabilities along the data flow, allowing for targeted security measures.
-
Assessing Data Sensitivity: Different types of personal data carry varying levels of sensitivity. Mapping should classify data based on its sensitivity, informing the level of security controls required. For example, sensitive personal data such as health information requires stricter protection than less sensitive data like email addresses.
3. Data Security Technologies: Investing in Robust Solutions
Meeting the stringent requirements of GDPR and CCPA necessitates investment in robust data security technologies. This goes beyond basic antivirus and firewalls to include:
-
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools: These tools monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control, whether through unauthorized email, cloud storage, or other channels.
-
Encryption: Encrypting data both in transit and at rest is essential to protect it from unauthorized access. This includes encryption of databases, cloud storage, and communication channels.
-
Access Control Mechanisms: Implementing strong access control measures, such as role-based access control (RBAC), ensures that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive data. This minimizes the risk of insider threats and unauthorized access.
-
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM systems collect and analyze security logs from various sources, providing real-time visibility into security events and enabling faster incident response.
4. Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs): A Proactive Approach
Beyond traditional security measures, GDPR and CCPA encourage the adoption of Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs). These technologies offer a proactive approach to data protection, minimizing the risk of data breaches and enhancing user privacy.
-
Differential Privacy: This technique adds carefully calibrated noise to datasets, making it difficult to identify individual data points while preserving the overall statistical properties of the data.
-
Federated Learning: This allows machine learning models to be trained on decentralized data without directly sharing the data itself, preserving privacy while enabling collaborative data analysis.
-
Homomorphic Encryption: This allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without decryption, enabling secure data processing without compromising confidentiality.
5. Incident Response Planning: Preparing for the Inevitable
Even with the best security measures in place, data breaches can still occur. Having a comprehensive incident response plan is therefore crucial for minimizing the impact of a breach and ensuring compliance with GDPR and CCPA. This plan should include:
-
A clear chain of command and communication protocols: This ensures efficient coordination during a crisis.
-
Procedures for identifying and containing the breach: This involves isolating affected systems and preventing further data loss.
-
Methods for notifying affected individuals and authorities: This must comply with the notification requirements of GDPR and CCPA.
-
A post-incident review process: This helps identify weaknesses in the security infrastructure and improve future preparedness.
6. Third-Party Risk Management: Extending Data Protection Beyond Internal Boundaries
GDPR and CCPA extend data protection responsibilities to third-party vendors and processors. Organizations must carefully vet their vendors and ensure they have adequate data security measures in place. This involves:
-
Due diligence: Thoroughly assessing the security practices of third-party vendors before entering into a contract.
-
Contractual agreements: Including strong data protection clauses in contracts with vendors, outlining their responsibilities and liabilities.
-
Regular audits: Conducting regular audits to ensure vendors are maintaining adequate security controls.
7. Data Subject Rights: Empowering Individuals and Building Trust
GDPR and CCPA grant individuals significant rights regarding their personal data, including the right to access, rectification, erasure, and data portability. Organizations must establish robust processes to handle these requests efficiently and transparently. This includes:
-
Clear and accessible data subject access request (DSAR) procedures: Individuals should be able to easily submit requests and receive timely responses.
-
Dedicated teams to handle DSARs: This ensures requests are processed efficiently and accurately.
-
Secure systems for handling DSARs: Protecting the privacy and security of individuals’ data during the DSAR process is crucial.
8. Ongoing Monitoring and Adaptation: A Continuous Improvement Cycle
Compliance with GDPR and CCPA is not a one-time event; it’s an ongoing process. Organizations must continually monitor their data security practices, adapt to evolving threats, and stay abreast of regulatory changes. This requires:
-
Regular security assessments: Conducting periodic vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify and address security weaknesses.
-
Staying informed about regulatory updates: Keeping up with changes in GDPR and CCPA regulations and adapting practices accordingly.
-
Continuous improvement: Using lessons learned from incidents and audits to improve data security practices over time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the main difference between GDPR and CCPA?
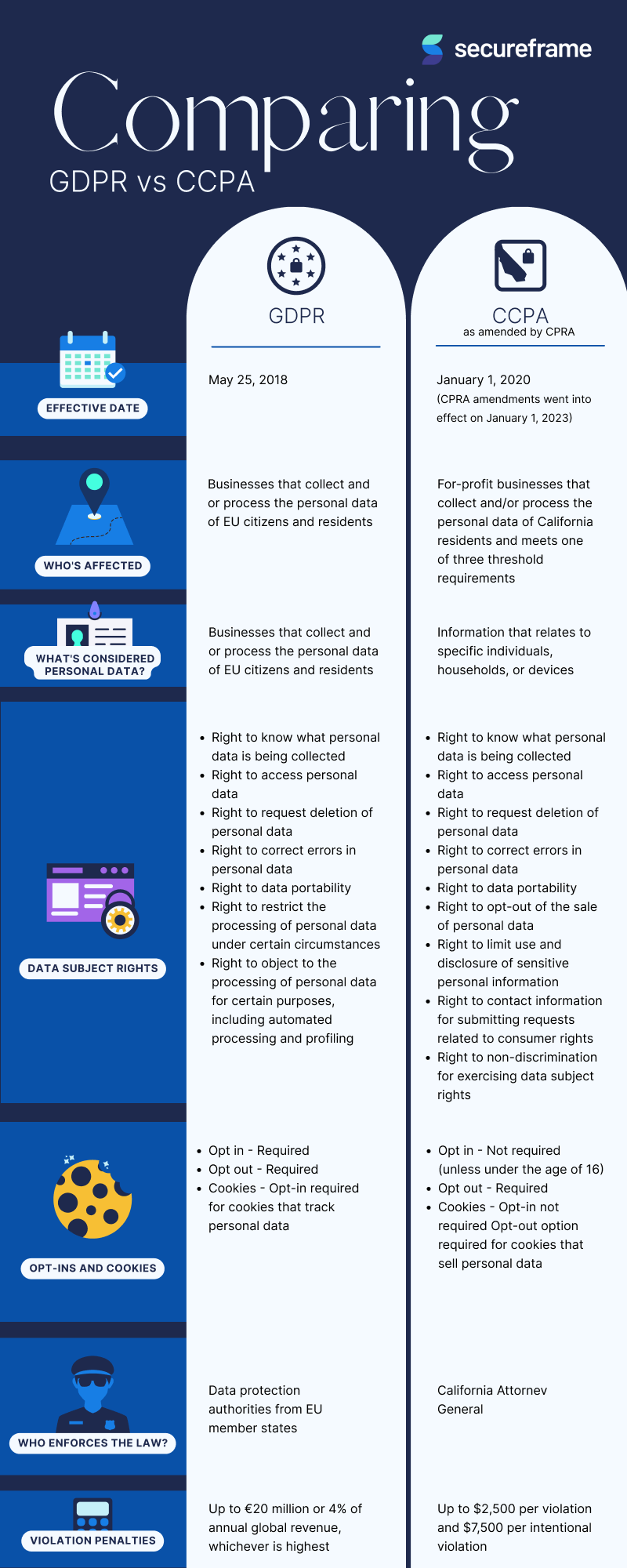
A1: While both aim to protect personal data, GDPR applies to organizations processing the personal data of individuals in the European Union, regardless of the organization’s location. CCPA, on the other hand, applies only to businesses operating in California and only protects the data of California residents. GDPR has a broader scope and stricter penalties.
Q2: What are the penalties for non-compliance with GDPR and CCPA?
A2: GDPR penalties can be substantial, reaching up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher. CCPA penalties are less severe but still significant, with potential fines of $2,500 per violation.
Q3: Do small businesses need to comply with GDPR and CCPA?
A3: Yes, businesses of all sizes that process personal data of EU residents (GDPR) or California residents (CCPA) are subject to these regulations. The specific requirements may vary based on the size and nature of the business, but compliance is mandatory.
Q4: How can I demonstrate compliance with GDPR and CCPA?
A4: Demonstrating compliance involves maintaining detailed records of data processing activities, implementing robust security measures, responding promptly to data subject requests, and having a comprehensive incident response plan. Regular audits and certifications can help provide evidence of compliance.
Q5: Is it possible to achieve 100% data security?
A5: No, achieving 100% data security is virtually impossible. However, by implementing robust security measures, fostering a culture of data security, and proactively addressing potential vulnerabilities, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and comply with GDPR and CCPA.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the impact of GDPR and CCPA on data security practices. Remember, proactive measures, a holistic approach, and continuous improvement are key to navigating this evolving landscape and building a trustworthy relationship with your customers.
Source URL: [Insert a relevant URL here, for example, a link to the official GDPR website or a reputable cybersecurity resource.]
Closure
Thank you for reading! Stay with us for more insights on “impact of GDPR and CCPA on data security practices”.
Don’t forget to check back for the latest news and updates on “impact of GDPR and CCPA on data security practices”!
We’d love to hear your thoughts about “impact of GDPR and CCPA on data security practices”—leave your comments below!
Keep visiting our website for the latest trends and reviews.
