Future of business data encryption after quantum computing
Related Articles
- “how To Balance Security And Usability In Enterprise Systems”
- “how Blockchain Can Enhance Data Security In Business”
- “how To Monitor Employee Devices For Potential Data Breaches”
- “essential Steps For Securing Remote Work Data In 2025”
- “importance Of Supply Chain Security In Preventing Data Breaches”
Introduction
Uncover the latest details about Future of business data encryption after quantum computing in this comprehensive guide.
The very algorithms that underpin modern encryption – RSA, ECC, and others – are vulnerable to the immense computational power of quantum computers. This looming threat necessitates a proactive and multifaceted approach to securing business data, moving beyond the current paradigm and embracing post-quantum cryptography (PQC). This article delves into the big secret tips and tricks, the cutting-edge strategies, and the crucial considerations for businesses navigating this transformative era.
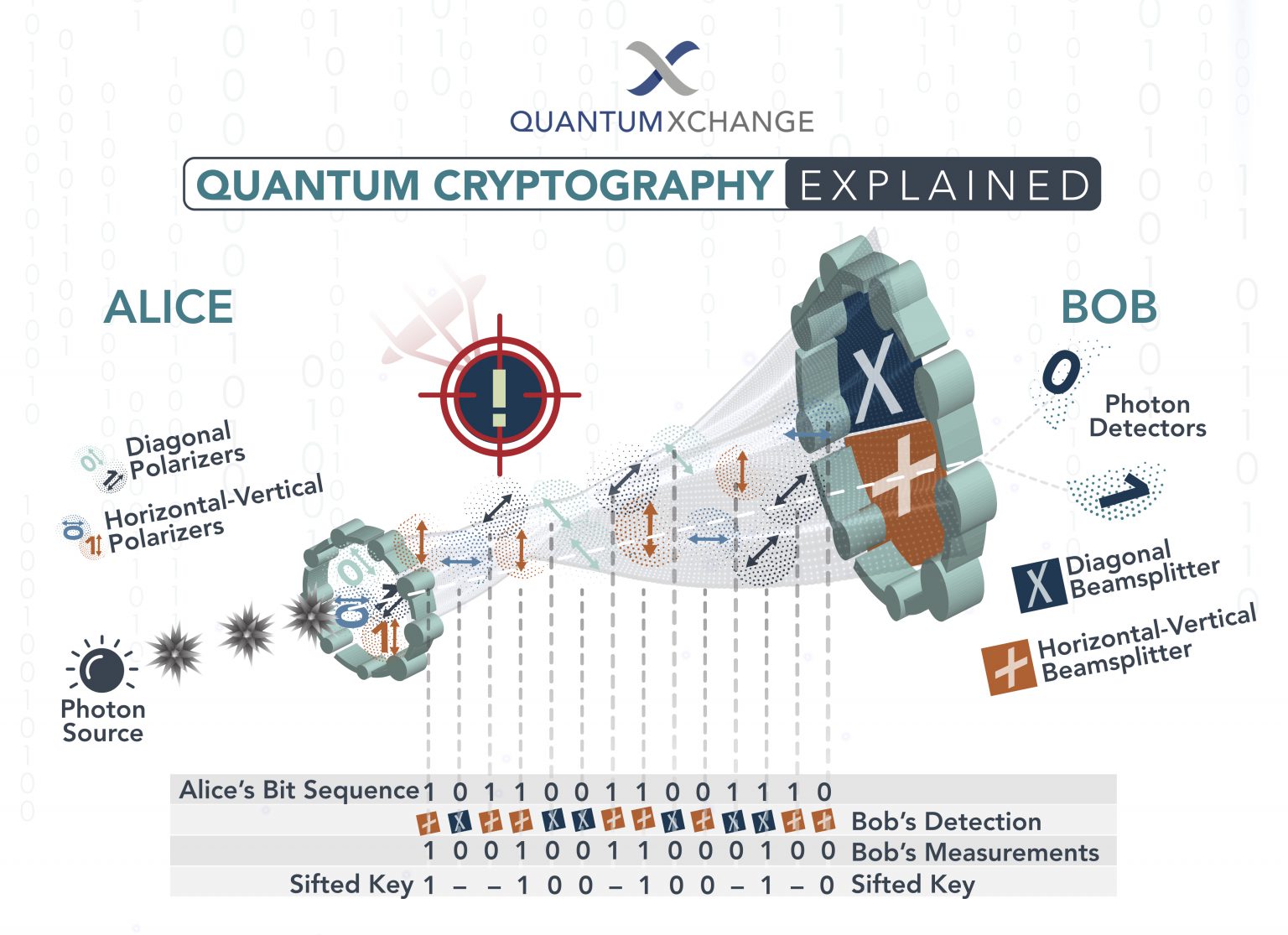
1. Understanding the Quantum Threat: More Than Just Faster Computers
Quantum computers don’t simply perform calculations faster than classical computers; they operate on fundamentally different principles. Leveraging quantum phenomena like superposition and entanglement, they can solve certain problems exponentially faster than their classical counterparts. This includes factoring large numbers – the very foundation of widely used public-key cryptography algorithms like RSA. This means that data currently secured by these algorithms could be easily decrypted by a sufficiently powerful quantum computer, exposing sensitive business information, intellectual property, and financial data to significant risk. The "secret" here isn’t a hidden algorithm, but a fundamental shift in understanding the threat. It’s not just about speed; it’s about the ability to break currently unbreakable codes.
The threat is not hypothetical. While fully fault-tolerant quantum computers are still some years away, research is progressing rapidly. Governments and large corporations are investing heavily in quantum computing research, and the potential for malicious actors to exploit vulnerabilities is a serious concern. The "secret" to preparedness lies in acknowledging this reality and acting decisively.
2. Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC): The New Shield
The solution lies in post-quantum cryptography (PQC), a branch of cryptography focused on developing algorithms resistant to attacks from both classical and quantum computers. These algorithms are based on mathematical problems believed to be intractable even for quantum computers. Several promising PQC candidates are currently under consideration by standardization bodies like NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology). The "secret" here is in understanding the diversity of these algorithms. There’s no single "magic bullet"; instead, a layered approach utilizing multiple PQC algorithms is likely to be the most effective strategy.
Some of the leading PQC candidates include:
- Lattice-based cryptography: Relies on the difficulty of finding short vectors in high-dimensional lattices.
- Code-based cryptography: Based on the difficulty of decoding random linear codes.
- Multivariate cryptography: Uses the difficulty of solving systems of multivariate polynomial equations.
- Hash-based cryptography: Uses cryptographic hash functions to create digital signatures.
- Isogeny-based cryptography: Relies on the difficulty of finding isogenies between elliptic curves.
The "trick" is to understand the strengths and weaknesses of each candidate and choose the most appropriate algorithm for specific applications and security needs. A diversified approach, employing different PQC algorithms for different purposes, significantly strengthens the overall security posture.
3. Hybrid Approaches: Bridging the Gap
Transitioning to PQC is not a simple switch. Implementing PQC requires significant effort, including updating systems, infrastructure, and applications. A hybrid approach, combining existing classical cryptography with PQC, offers a practical solution during the transition period. This involves using classical algorithms for current operations while gradually integrating PQC for long-term security. The "secret" lies in strategically phasing in PQC, prioritizing sensitive data and critical systems.
This hybrid approach allows businesses to maintain a robust security posture while mitigating the risk of a complete system overhaul. It also allows for testing and evaluation of PQC algorithms in real-world scenarios, providing valuable experience before a full-scale deployment.
4. Key Management: The Achilles Heel of PQC Implementation
Key management is paramount in any cryptographic system, and PQC is no exception. Securely generating, storing, and managing cryptographic keys is crucial to maintaining the integrity of the encryption system. The "secret" to effective key management lies in adopting robust key management systems (KMS) designed to protect against both classical and quantum attacks.
This includes implementing secure key generation protocols, utilizing hardware security modules (HSMs) for key storage, and employing strict access control measures. Failing to secure keys renders even the most robust PQC algorithms vulnerable. Therefore, investing in advanced key management infrastructure is a critical step in preparing for the post-quantum era.
5. Quantum-Resistant Hardware: The Foundation of Future Security
While software-based PQC is crucial, the future of secure computing lies in quantum-resistant hardware. This includes specialized processors designed to accelerate PQC algorithms and hardware security modules (HSMs) that protect cryptographic keys from both physical and digital attacks. The "secret" is recognizing that hardware plays a pivotal role. Software alone is insufficient. A holistic approach encompassing both software and hardware is essential for comprehensive security.
Investing in quantum-resistant hardware is a long-term strategy but a necessary one. It provides a more secure foundation for data protection, mitigating the risk of vulnerabilities in software implementations. This includes exploring technologies like homomorphic encryption, which allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without decryption.
6. Regulatory Compliance and Standards: Navigating the Legal Landscape
The emergence of PQC brings new regulatory and compliance challenges. Businesses need to understand and comply with emerging standards and regulations related to post-quantum cryptography. The "secret" lies in staying informed about evolving standards and proactively adapting to them. This includes staying abreast of NIST’s PQC standardization efforts and other relevant regulatory developments.
Failure to comply with these standards can lead to significant legal and financial penalties. Proactive engagement with regulatory bodies and industry best practices is crucial for maintaining compliance and minimizing risk.
7. Education and Training: The Human Factor
The success of any security measure hinges on the human element. Educating and training employees about the risks of quantum computing and the importance of PQC is crucial. The "secret" is recognizing that people are the weakest link in any security system. Comprehensive training programs that cover the basics of quantum computing, PQC, and best security practices are essential.
This includes educating employees on secure password management, phishing awareness, and other security best practices. A well-informed workforce is a more resilient workforce, better equipped to identify and respond to emerging threats.
8. Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation: A Dynamic Approach
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving. The transition to PQC is an ongoing process, not a one-time event. Continuous monitoring, threat assessment, and adaptation are crucial to maintaining a robust security posture. The "secret" is embracing a dynamic approach to security. Regularly updating systems, monitoring for vulnerabilities, and adapting to emerging threats are essential for long-term success.
This includes staying informed about advancements in quantum computing and PQC, regularly reviewing security protocols, and conducting penetration testing to identify and address weaknesses. A proactive and adaptive approach is vital in this rapidly changing environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: When will quantum computers pose a real threat to current encryption?
A1: While fully fault-tolerant quantum computers are still years away, the timeline is uncertain. Research is progressing rapidly, and it’s crucial to start preparing now rather than waiting for a definitive threat.
Q2: Is migrating to PQC a simple process?
A2: No. It requires significant planning, testing, and implementation effort. A phased approach using hybrid cryptography is recommended.
Q3: Which PQC algorithm is the best?
A3: There’s no single "best" algorithm. The optimal choice depends on the specific application and security requirements. A diversified approach is often preferred.
Q4: How much will migrating to PQC cost?
A4: The cost varies greatly depending on the size and complexity of the organization’s systems. It’s a significant investment, but the cost of a data breach far outweighs the cost of proactive migration.
Q5: What role does the cloud play in PQC implementation?
A5: Cloud providers are playing a significant role in developing and deploying PQC solutions. Many offer PQC-based services, simplifying the migration process for businesses.
Q6: What are the ethical considerations of quantum computing and PQC?
A6: The development and deployment of quantum computing and PQC raise ethical concerns regarding access, control, and potential misuse. Careful consideration of these issues is crucial.
The future of business data encryption is inextricably linked to the development of quantum computing. By understanding the threat, embracing PQC, and adopting a proactive and multifaceted approach, businesses can secure their data and navigate this transformative era successfully. The "secrets" revealed in this article are not about hidden algorithms but about strategic planning, technological innovation, and a commitment to robust cybersecurity practices.
Source URL: [Insert a relevant URL here, e.g., a NIST publication on PQC or an article from a reputable cybersecurity publication]
Closure
Thank you for reading! Stay with us for more insights on Future of business data encryption after quantum computing.
Make sure to follow us for more exciting news and reviews.
We’d love to hear your thoughts about Future of business data encryption after quantum computing—leave your comments below!
Keep visiting our website for the latest trends and reviews.
