Best practices for securing multi-cloud environments 2025
Related Articles
- Cyber Insurance Trends For Small Businesses 2025
- How To Safeguard Financial Data From Phishing Attacks
- How To Educate Employees About Data Phishing Tactics In 2025
- Zero Trust Architecture For Small Businesses
- Top Cybersecurity Certifications For Data Professionals In 2025
Introduction
Uncover the latest details about Best practices for securing multi-cloud environments 2025 in this comprehensive guide.
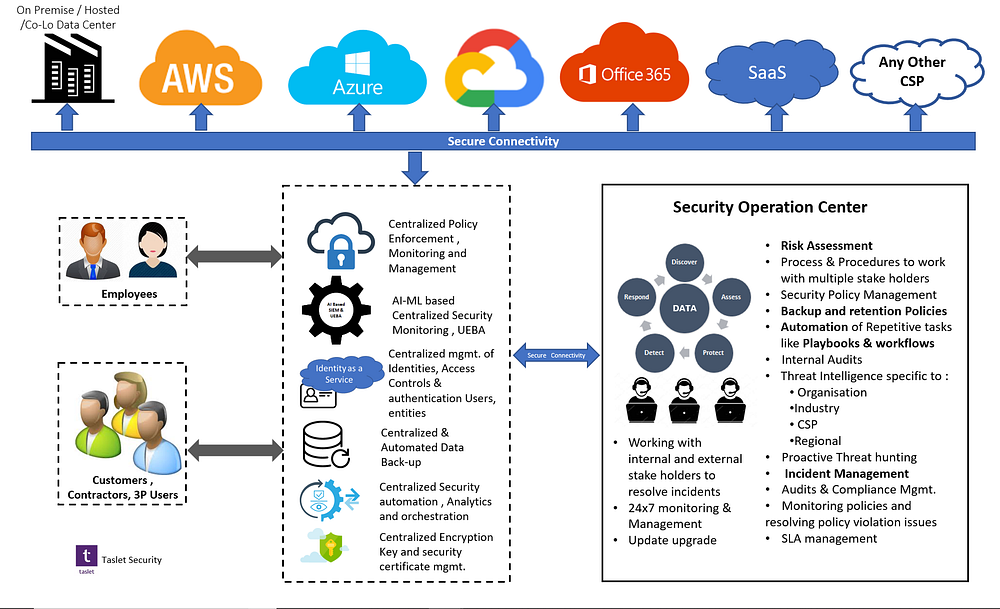
However, this distributed architecture introduces significant security complexities. Simply replicating on-premises security strategies across multiple cloud providers is insufficient. To thrive in 2025 and beyond, organizations must adopt proactive, sophisticated security measures tailored to the unique challenges of a multi-cloud environment. This article delves into the "big secret" tips and tricks – often overlooked best practices – for securing your multi-cloud infrastructure.
1. Beyond the Perimeter: Zero Trust Architecture is Non-Negotiable
The traditional "castle-and-moat" security model, relying on a perimeter firewall, is obsolete in the multi-cloud world. Data resides across numerous environments, making perimeter security ineffective. Zero Trust architecture is the cornerstone of multi-cloud security in 2025. This model assumes no implicit trust and verifies every user, device, and application before granting access to resources, regardless of location.
Secret Tip: Don’t just implement Zero Trust – optimize it. Leverage granular access controls based on attributes like user role, device posture, and location. Implement continuous monitoring and anomaly detection to identify and respond to unauthorized access attempts swiftly. Consider integrating behavioral analytics to profile normal user activity and flag deviations.
Trick: Implement a robust identity and access management (IAM) system that supports single sign-on (SSO) across all your cloud providers. This simplifies user management and strengthens security by reducing the number of credentials users need to manage. Explore federated identity solutions for seamless integration with on-premises systems.
2. Data Security: Encryption, Discovery, and Classification are Crucial
Data is the lifeblood of any organization, and securing it in a multi-cloud environment is paramount. Encryption should be employed at rest, in transit, and even in use where feasible. Data discovery and classification tools are essential for identifying sensitive data residing across various clouds. This allows for targeted protection strategies based on data sensitivity levels.
Secret Tip: Embrace data loss prevention (DLP) solutions that integrate with your cloud providers’ security services. These tools can monitor data movement and prevent sensitive data from leaving your environment unauthorized. Implement robust key management practices, including hardware security modules (HSMs) for securing encryption keys.
Trick: Don’t rely solely on cloud provider-managed encryption. Implement your own encryption layers for added security and control. Consider using encryption techniques like homomorphic encryption for processing sensitive data without decryption.
3. Cloud-Native Security Tools: Embrace the Power of Automation
Cloud providers offer a range of security services specifically designed for their platforms. Leveraging these cloud-native tools is crucial for efficient and effective security management. These tools often integrate seamlessly with other cloud services, enabling automation of security tasks such as vulnerability scanning, intrusion detection, and incident response.

Secret Tip: Don’t just use individual cloud security services; integrate them across your multi-cloud environment. Use cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools to gain a holistic view of your security posture across all clouds. Automate security tasks using Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) and DevOps practices.
Trick: Utilize cloud-native security information and event management (SIEM) solutions for centralized logging and monitoring across all your cloud environments. This provides a single pane of glass for security monitoring and incident response.
4. Vulnerability Management: Continuous Scanning and Remediation
Vulnerabilities are inevitable in any IT infrastructure. In a multi-cloud environment, the attack surface is significantly larger, making vulnerability management critical. Implement continuous vulnerability scanning and remediation processes across all your cloud platforms.
Secret Tip: Prioritize vulnerabilities based on their severity and potential impact. Don’t just focus on known vulnerabilities; employ techniques like static and dynamic application security testing (SAST/DAST) to identify unknown vulnerabilities in your applications.
Trick: Automate vulnerability remediation using IaC and configuration management tools. Integrate vulnerability scanning with your CI/CD pipeline to identify and address vulnerabilities early in the software development lifecycle.
5. Network Security: Microsegmentation and Secure Connectivity
Securing network traffic across multiple cloud environments requires a sophisticated approach. Microsegmentation divides your network into smaller, isolated segments, limiting the impact of a breach. Secure connectivity ensures that communication between different cloud environments and on-premises systems is protected.
Secret Tip: Implement network segmentation based on application, data sensitivity, and user roles. Utilize virtual private clouds (VPCs) and virtual private networks (VPNs) to create secure connections between your cloud environments. Consider using service meshes for secure communication between microservices.
Trick: Employ advanced network security tools like intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) and web application firewalls (WAFs) to protect your network from threats. Implement traffic filtering and monitoring to identify and block malicious activity.
6. Compliance and Governance: A Multi-Cloud Challenge
Navigating the complex compliance landscape across multiple cloud providers is a significant challenge. Each cloud provider has its own set of security and compliance standards. Establish a robust compliance and governance framework to ensure that your multi-cloud environment meets all relevant regulations.
Secret Tip: Implement a centralized compliance management system that tracks compliance across all your cloud environments. Automate compliance checks using IaC and configuration management tools. Use cloud-native compliance tools offered by your cloud providers.
Trick: Develop a comprehensive compliance policy that outlines your organization’s security requirements and responsibilities. Regularly audit your multi-cloud environment to ensure compliance with your policies and relevant regulations.
7. Security Monitoring and Incident Response: Proactive Defense
Continuous monitoring is essential for identifying and responding to security incidents promptly. Implement a comprehensive security monitoring strategy that covers all aspects of your multi-cloud environment. Develop an incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a security breach.
Secret Tip: Utilize security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) tools to automate incident response tasks. Regularly test your incident response plan to ensure its effectiveness. Establish clear communication channels for coordinating incident response activities.
Trick: Invest in security analytics tools that can analyze security logs and identify anomalies that may indicate a security breach. Implement threat intelligence feeds to stay informed about emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
8. People and Processes: The Human Element of Security
Security is not just about technology; it’s also about people and processes. Invest in security awareness training for your employees to educate them about the risks associated with multi-cloud environments. Establish clear security policies and procedures that are consistently enforced.
Secret Tip: Conduct regular security awareness training that is tailored to the specific risks associated with multi-cloud environments. Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users to enhance security. Establish a security incident response team with clearly defined roles and responsibilities.
Trick: Use gamification techniques to make security training more engaging and effective. Establish a culture of security within your organization, where employees are empowered to report security concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the biggest security challenge in a multi-cloud environment?
A: The biggest challenge is the increased complexity and distributed nature of the environment, making it difficult to maintain a consistent security posture across all clouds.
Q: How can I ensure consistent security policies across multiple cloud providers?
A: Implement a centralized security management system and leverage cloud-native security tools that integrate across your multi-cloud environment. Use Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) to enforce consistent configurations.
Q: What are the key benefits of a Zero Trust architecture in a multi-cloud environment?
A: Zero Trust eliminates implicit trust, minimizing the impact of breaches by limiting lateral movement. It provides granular access control and continuous monitoring, enhancing overall security.
Q: How can I effectively manage compliance across multiple cloud providers?
A: Establish a centralized compliance management system, leverage cloud-native compliance tools, and automate compliance checks using IaC. Develop a comprehensive compliance policy and conduct regular audits.
Q: What is the role of automation in multi-cloud security?
A: Automation is crucial for streamlining security tasks, improving efficiency, and reducing human error. It enables continuous monitoring, vulnerability management, and incident response.
By embracing these "big secret" tips and tricks, organizations can effectively navigate the complexities of multi-cloud security in 2025 and beyond. Remember that security is an ongoing journey, not a destination. Continuous monitoring, adaptation, and improvement are essential for maintaining a robust and resilient multi-cloud security posture.
Source URL: [Insert a relevant URL from a reputable cybersecurity source here, e.g., a NIST publication or a major cybersecurity vendor’s website]
Closure
We hope this article has helped you understand everything about Best practices for securing multi-cloud environments 2025. Stay tuned for more updates!
Don’t forget to check back for the latest news and updates on Best practices for securing multi-cloud environments 2025!
We’d love to hear your thoughts about Best practices for securing multi-cloud environments 2025—leave your comments below!
Stay informed with our next updates on Best practices for securing multi-cloud environments 2025 and other exciting topics.