“best practices for securing business data backups”
Related Articles
- “top Data Breach Prevention Tools For Businesses 2025”
- “how To Detect And Prevent Fileless Malware Attacks”
- “cybersecurity Strategies For Startup Businesses In The US”
- “2025 Guide To Choosing The Best Cybersecurity Insurance”
- “top Cybersecurity Measures For The Financial Industry 2025”
Introduction
Join us as we explore “best practices for securing business data backups”, packed with exciting updates
Losing it – whether through accidental deletion, ransomware attacks, hardware failure, or natural disaster – can be catastrophic, potentially leading to financial ruin, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. While regular backups are crucial for business continuity, simply creating backups isn’t enough. Securing those backups is equally, if not more, important. This article delves into the often-overlooked best practices for securing your business data backups, revealing the "big secret" tips and tricks that ensure your data remains safe and recoverable.
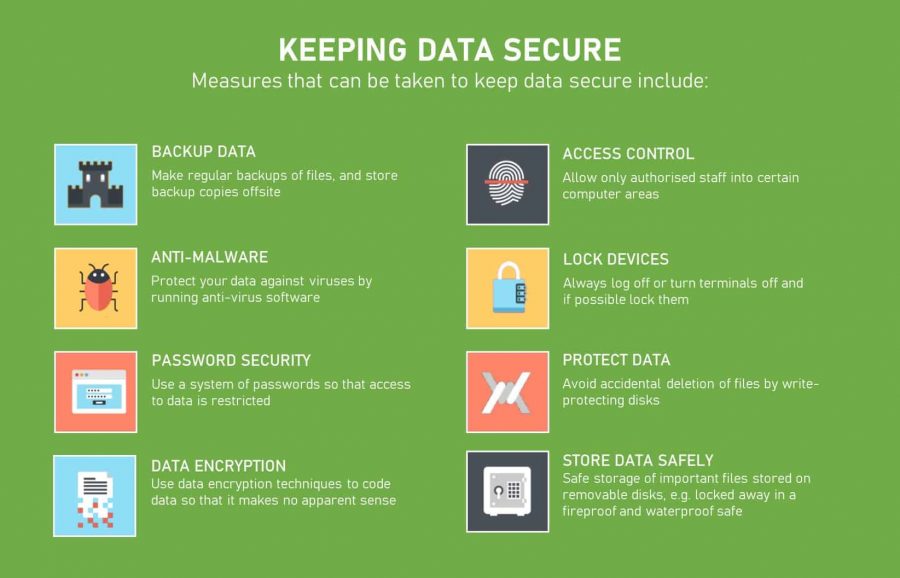
1. The 3-2-1 Backup Rule: The Foundation of Data Security
The 3-2-1 rule is the cornerstone of any robust backup strategy. It dictates that you should have:
- 3 Copies of your data: This redundancy ensures data survivability even if one copy is compromised. These copies can be spread across different backup methods (e.g., local, cloud, tape).
- 2 Different Storage Media: Don’t rely on a single storage type. Use a combination of local drives (HDD or SSD), cloud storage, and perhaps even offsite tape backups. This mitigates risks associated with specific hardware failures or vulnerabilities.
- 1 Offsite Backup: This is critically important. An offsite backup protects your data from local disasters such as fire, flood, or theft. Cloud storage is an excellent option for offsite backups, but physical offsite storage in a geographically separate location is also valuable.
The 3-2-1 rule is not just a suggestion; it’s a fundamental requirement for any business serious about data protection. Failing to adhere to it significantly increases your risk of irreversible data loss.
2. Encryption: The Unsung Hero of Backup Security
Encryption is paramount for securing your backups. Without it, your data is vulnerable if your backup media is lost or stolen. Encryption transforms your data into an unreadable format, requiring a decryption key to access it. Employ strong encryption algorithms like AES-256 for maximum protection.

- Full Disk Encryption: For local backups, consider full disk encryption on the storage device itself. This protects the data even if the device is physically compromised.
- File-Level Encryption: For cloud backups or network-attached storage (NAS), file-level encryption ensures individual files are encrypted before being stored.
- Key Management: Securely manage your encryption keys. Use strong passwords, key management systems, or hardware security modules (HSMs) to protect against unauthorized access. Never store the encryption key on the same device as the encrypted data.
Remember, encryption is not just about protecting against theft; it also helps meet compliance requirements (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) that mandate data protection.
3. Access Control and Authentication: Limiting the Gatekeepers
Restricting access to your backups is as crucial as encrypting them. Implement robust access control mechanisms to prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing or modifying your backup data.
- Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Use strong, unique passwords for all backup systems and accounts. Implement MFA whenever possible to add an extra layer of security.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Define roles and assign permissions based on those roles. Only authorized personnel should have access to backup systems and data.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular security audits to ensure that access controls are working effectively and that no unauthorized access has occurred.
Limiting access prevents accidental or malicious data deletion, modification, or exfiltration.
4. Versioning and Immutable Backups: Protecting Against Ransomware
Ransomware attacks are a major threat to businesses. One effective defense is versioning and immutable backups.
- Versioning: This creates multiple versions of your backups over time, allowing you to revert to an earlier version if a backup is compromised. Cloud storage services often provide built-in versioning features.
- Immutable Backups: These backups cannot be modified or deleted once they are created. This prevents ransomware from encrypting or deleting your backups, ensuring data recoverability. Many cloud providers and backup solutions offer immutable storage options.
By combining versioning and immutable backups, you create a powerful defense against ransomware, significantly reducing the impact of an attack.
5. Regular Testing and Recovery Drills: Proactive Prevention is Key
Regular testing and recovery drills are often overlooked but are critical for ensuring your backup strategy works as intended.
- Test Restores: Periodically test the restoration process to verify that you can successfully recover your data. This identifies any issues with your backup procedures or infrastructure before a real disaster strikes.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO): Define your RTO (how long it takes to recover your data) and RPO (how much data you can afford to lose) to guide your backup strategy and testing.
- Documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation of your backup procedures, including the location of backups, encryption keys, and recovery steps. This ensures that anyone can restore your data in case of an emergency.
Proactive testing ensures you can recover your data quickly and efficiently in a real-world scenario.
6. Choosing the Right Backup Solution: A Tailored Approach
Selecting the appropriate backup solution is crucial for effective data protection. Consider factors such as:
- Scalability: Choose a solution that can scale to meet your growing data needs.
- Security Features: Ensure the solution offers robust security features, including encryption, access control, and versioning.
- Integration: Consider how well the solution integrates with your existing IT infrastructure.
- Cost: Balance cost with the level of protection offered.
There’s no one-size-fits-all solution. Evaluate your specific needs and choose a solution that best addresses them.
7. Monitoring and Alerting: Staying Vigilant
Continuous monitoring and alerting are essential for proactive security management.
- Backup Monitoring: Implement monitoring tools to track backup jobs, ensuring they complete successfully. Alert on failures or anomalies.
- Security Monitoring: Monitor your backup systems for suspicious activity, such as unauthorized access attempts or unusual data modifications.
- Log Analysis: Regularly analyze logs from your backup systems to identify potential security issues.
Proactive monitoring enables swift response to potential threats and minimizes downtime.
8. Employee Training: The Human Factor
Your employees are your first line of defense. Educate them on the importance of data security and best practices for handling sensitive information.
- Security Awareness Training: Provide regular training on topics such as phishing, malware, and social engineering.
- Backup Procedures: Train employees on proper backup procedures and the importance of reporting any suspicious activity.
- Data Handling Policies: Establish clear data handling policies and ensure employees understand and adhere to them.
A well-trained workforce is less likely to fall victim to social engineering attacks or make mistakes that compromise data security.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the best backup solution for my business?
A: The best solution depends on your specific needs, budget, and technical expertise. Consider factors such as data volume, RTO/RPO requirements, budget, and the level of technical expertise within your organization. Options range from simple local backups to sophisticated cloud-based solutions.
Q: How often should I perform backups?
A: The frequency depends on your data change rate and RPO. For critical data, consider hourly or even continuous backups. For less critical data, daily or weekly backups might suffice.
Q: What if my backup media is lost or stolen?
A: Encryption protects your data even if the media is lost or stolen. If you haven’t encrypted your backups, the data is vulnerable. Having multiple copies and an offsite backup minimizes the risk.
Q: How can I ensure my backups are truly secure?
A: Follow the 3-2-1 rule, implement strong encryption, restrict access, use versioning and immutable backups, regularly test restores, and monitor your backup systems.
Q: What are the legal implications of not securing my backups?
A: Failure to adequately secure business data can lead to significant legal repercussions, particularly if you handle sensitive personal or financial information. Regulations like GDPR and HIPAA impose strict data protection requirements. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and legal action.
Q: How can I balance security with cost-effectiveness?
A: Start with the fundamentals – the 3-2-1 rule and encryption. Then, prioritize based on your risk assessment. Consider cloud-based solutions for cost-effectiveness, but ensure they meet your security requirements.
Q: What are the key indicators of a successful backup strategy?
A: A successful backup strategy results in readily available, secure, and easily recoverable data. Regular testing, minimal downtime during recovery, and adherence to your RTO/RPO are key indicators.
By implementing these best practices, businesses can significantly enhance the security of their data backups, reducing the risk of data loss and ensuring business continuity. Remember, data security is an ongoing process, requiring continuous vigilance and adaptation to evolving threats.
Source URL: [Insert a relevant URL here, for example, a NIST publication on data backup security or a reputable cybersecurity firm’s website discussing backup best practices.] For example: [https://www.nist.gov/](Replace with actual URL)
Closure
We hope this article has helped you understand everything about “best practices for securing business data backups”. Stay tuned for more updates!
Make sure to follow us for more exciting news and reviews.
We’d love to hear your thoughts about “best practices for securing business data backups”—leave your comments below!
Keep visiting our website for the latest trends and reviews.
