How to implement Zero Trust in cloud computing
Related Articles
- “emerging Cybersecurity Solutions For Protecting Intellectual Property”
- “how 5G Technology Affects Business Data Security”
- How To Comply With U.S. Cybersecurity Regulations In 2025
- “how To Secure IoT Devices In Your Business Network”
- “impact Of Quantum Computing On Business Data Encryption”
Introduction
Discover everything you need to know about How to implement Zero Trust in cloud computing
Traditional perimeter-based security models, which rely on a "castle-and-moat" approach, are woefully inadequate in this environment. This is where Zero Trust comes in. Zero Trust, the revolutionary security framework, assumes no implicit trust and verifies every user and device before granting access to resources, regardless of location. Implementing Zero Trust in the cloud, however, isn’t a simple switch flip. It requires a nuanced understanding of your environment, meticulous planning, and a commitment to continuous monitoring and adaptation. This article delves into the big secret tips and tricks to successfully implement Zero Trust in your cloud infrastructure.
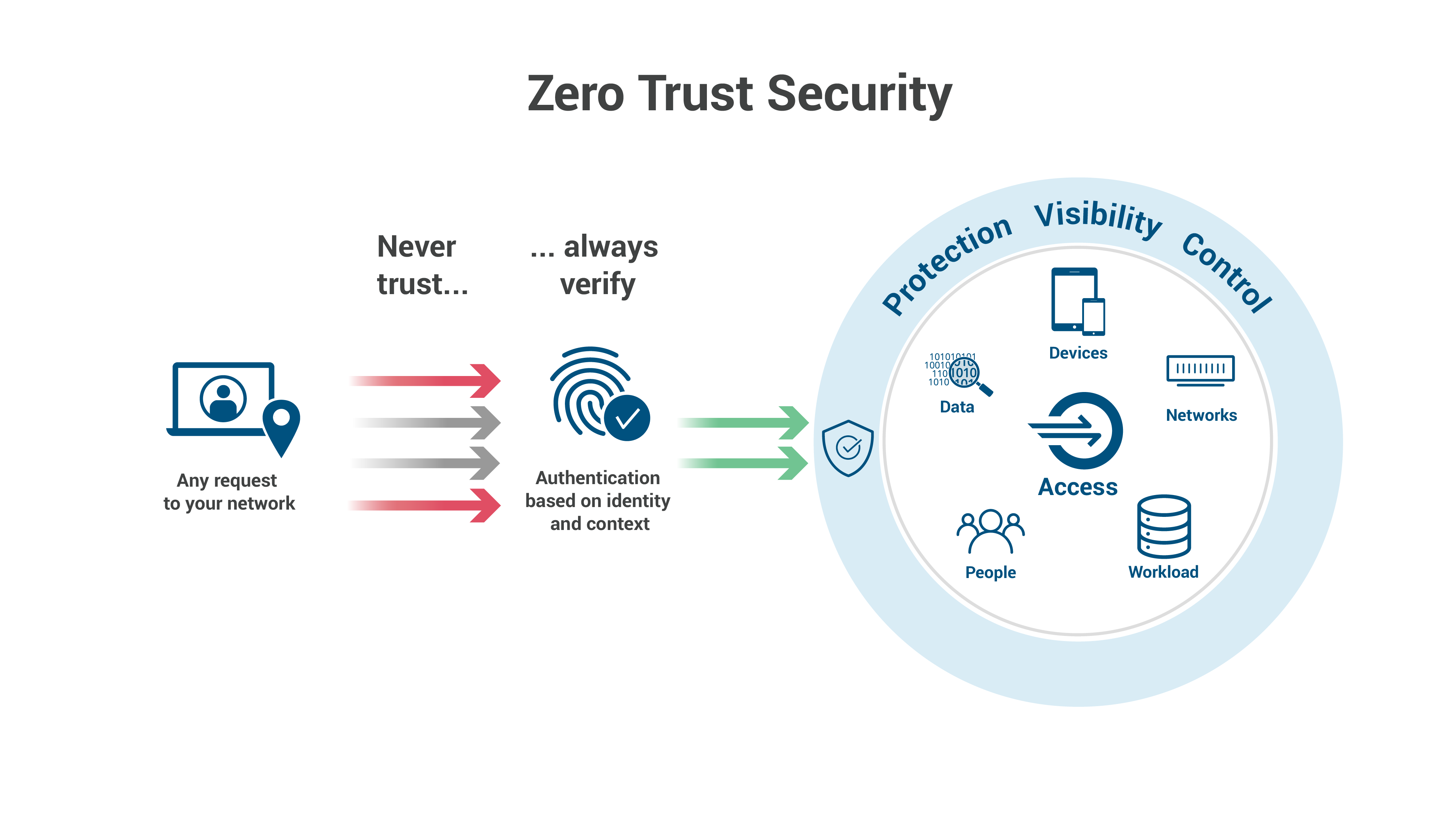
1. Beyond the Hype: Defining Your Zero Trust Strategy
Before diving into technical implementations, you need a clear, well-defined Zero Trust strategy. This isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution; it must be tailored to your specific organization’s needs, risk tolerance, and existing infrastructure. The "secret sauce" here lies in understanding your critical assets and prioritizing them for protection.
-
Identify Your Crown Jewels: What data and applications are most valuable to your business? These are your highest priority targets for Zero Trust protection. Knowing this allows you to focus resources effectively. Don’t try to secure everything at once; prioritize based on risk and impact.
-
Risk Assessment and Mapping: Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential vulnerabilities and attack vectors. Map your cloud environment, including all users, devices, applications, and data flows. This provides a baseline for your Zero Trust implementation.
Define Your Trust Boundaries: Traditional security focuses on a network perimeter. Zero Trust eliminates this concept. Instead, you define trust boundaries around individual resources, applications, and data sets. This granular approach allows for more precise control and minimizes the impact of breaches.
-
Choose Your Zero Trust Model: There are several approaches to Zero Trust, including network-centric, data-centric, and user-centric. The best approach depends on your specific needs and infrastructure. Consider a hybrid model if necessary, combining elements of different approaches.
2. Identity and Access Management (IAM): The Cornerstone of Zero Trust
IAM is the foundation of any successful Zero Trust implementation. It’s not just about usernames and passwords; it’s about establishing strong authentication, authorization, and continuous monitoring of user access. The "secret" here is to leverage advanced IAM capabilities offered by cloud providers.
-
Least Privilege Access: Grant users only the minimum level of access necessary to perform their jobs. Avoid granting broad administrative privileges unless absolutely essential. Regularly review and revoke unnecessary access rights.
-
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA for all users, including administrators. This adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access. Consider using a variety of MFA methods (e.g., hardware tokens, biometrics, one-time passwords).
-
Identity Federation: Integrate your cloud IAM with your on-premises identity provider (IdP) to streamline user management and authentication. This simplifies access control for users who need to access both cloud and on-premises resources.
-
Just-in-Time (JIT) Access: Grant temporary access to resources only when needed. This minimizes the window of vulnerability and reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
-
Privileged Access Management (PAM): Implement robust PAM solutions to manage and control access to sensitive systems and data by privileged users. This includes strong authentication, session recording, and auditing.
3. Microsegmentation: Dividing and Conquering Your Cloud Environment
Microsegmentation is the art of dividing your cloud environment into smaller, isolated segments. This limits the impact of a breach by preventing attackers from moving laterally across your network. The "secret" here is to leverage cloud-native tools and technologies for efficient and granular control.
-
Network Virtualization: Use virtual networks (VNs) and subnets to isolate different parts of your cloud environment. This allows you to create separate security zones for different applications and data sets.
-
Software-Defined Networking (SDN): SDN provides dynamic and programmable control over your network traffic, allowing you to implement fine-grained access control policies.
-
Micro-VMs: Consider using micro-VMs or containers to further isolate applications and services. This reduces the attack surface and minimizes the impact of a compromise.
-
Automated Segmentation: Automate the process of creating and managing network segments using tools and scripts. This ensures consistency and reduces manual errors.
4. Data Security: Protecting Your Most Valuable Asset
Data is the lifeblood of any organization. Securing your data in the cloud requires a multi-layered approach that goes beyond simple encryption. The "secret" here lies in combining various security controls to create a robust defense.
-
Data Encryption at Rest and in Transit: Encrypt data both when it’s stored and when it’s being transmitted. Use strong encryption algorithms and key management solutions.
-
Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implement DLP tools to prevent sensitive data from leaving your cloud environment without authorization. This includes monitoring data transfers and blocking unauthorized access attempts.
-
Access Control Lists (ACLs): Use ACLs to control access to individual data objects. This allows you to grant fine-grained access permissions to different users and groups.
-
Data Masking and Anonymization: Mask or anonymize sensitive data when it’s not needed for business purposes. This reduces the risk of data breaches and protects sensitive information.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection: The Ever-Vigilant Guardian
Zero Trust is not a one-time implementation; it’s a continuous process of monitoring, adapting, and improving your security posture. The "secret" here is to leverage advanced security information and event management (SIEM) and security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) tools.
-
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Use SIEM tools to collect and analyze security logs from various sources. This helps you detect and respond to security threats in real-time.
-
Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR): Automate security tasks, such as incident response and threat hunting, using SOAR tools. This improves efficiency and reduces response times.
-
Threat Intelligence: Stay informed about the latest threats and vulnerabilities by subscribing to threat intelligence feeds. This helps you proactively identify and mitigate potential risks.
-
Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to assess your security posture and identify areas for improvement. This helps you ensure that your Zero Trust implementation is effective.
6. Cloud-Native Security Tools: Leveraging the Power of the Platform
Cloud providers offer a wealth of security tools and services that can significantly enhance your Zero Trust implementation. The "secret" here is to understand and leverage these tools effectively.
-
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs): CASBs provide visibility and control over cloud applications and data. They can enforce security policies and prevent unauthorized access.
-
Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPPs): CWPPs protect your cloud workloads from threats. They can monitor and control access to virtual machines and containers.
-
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): CSPM tools help you assess and improve your cloud security posture. They can identify misconfigurations and vulnerabilities.
-
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Deploy IDPS in your cloud environment to detect and prevent malicious activity.
7. Automation and Orchestration: The Engine of Efficiency
Implementing and managing Zero Trust effectively requires automation. The "secret" is to automate as many aspects of your security operations as possible, freeing up your security team to focus on more strategic tasks.
-
Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC): Use IaC to automate the provisioning and management of your cloud infrastructure. This ensures consistency and reduces manual errors.
-
Automated Security Policies: Automate the creation and enforcement of security policies. This ensures that your security controls are consistently applied.
-
Automated Response to Threats: Automate the response to security threats, such as blocking malicious IP addresses or isolating infected systems.
8. People and Process: The Human Element of Zero Trust
Technology is only part of the equation. Zero Trust requires a cultural shift within your organization. The "secret" is to invest in training and awareness programs to ensure that your employees understand and comply with Zero Trust policies.
-
Security Awareness Training: Educate your employees about the importance of Zero Trust and how to protect themselves from cyber threats.
-
Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to handle security incidents effectively.
-
Regular Security Assessments: Conduct regular security assessments to identify areas for improvement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is Zero Trust a replacement for traditional security measures?
A: No, Zero Trust complements traditional security measures. It enhances existing security controls rather than replacing them entirely.
Q: How much does it cost to implement Zero Trust?
A: The cost varies depending on your organization’s size, complexity, and existing infrastructure. It’s an investment, but the cost of a breach far outweighs the cost of implementation.
Q: How long does it take to implement Zero Trust?
A: Implementation time depends on your organization’s size and complexity. It’s an iterative process, not a single event.
Q: What are the biggest challenges in implementing Zero Trust?
A: Challenges include complexity, cost, integrating with legacy systems, and the need for skilled personnel.
Q: Can I implement Zero Trust in a hybrid cloud environment?
A: Yes, Zero Trust principles can be applied to hybrid cloud environments, requiring careful coordination of on-premises and cloud security controls.
Implementing Zero Trust is a journey, not a destination. It requires ongoing commitment, adaptation, and a willingness to embrace new technologies and approaches. By focusing on the strategies and tactics outlined above, you can significantly enhance your cloud security posture and protect your organization from evolving cyber threats. Remember that consistent monitoring, adaptation, and employee training are crucial for long-term success.
Source URL: [Insert a relevant URL from a reputable cybersecurity website here, for example, a NIST publication or a major cloud provider’s security documentation.]
Closure
We hope this article has helped you understand everything about How to implement Zero Trust in cloud computing. Stay tuned for more updates!
Make sure to follow us for more exciting news and reviews.
We’d love to hear your thoughts about How to implement Zero Trust in cloud computing—leave your comments below!
Keep visiting our website for the latest trends and reviews.
