“2025 trends in ransomware attacks targeting small businesses”
Related Articles
- “best Cloud Storage Options For Secure Business Data 2025”
- “future-proofing Your Business Against Quantum Hacking”
- “data Security Trends For Financial Institutions In 2025”
- “how To Prevent Double-extortion Ransomware Attacks”
- “how To Secure IoT Devices In Corporate Networks”
Introduction
Welcome to our in-depth look at “2025 trends in ransomware attacks targeting small businesses”
While large corporations often have dedicated cybersecurity teams and robust infrastructure, smaller businesses frequently lack these resources, making them vulnerable and attractive to cybercriminals. Predicting the future of ransomware is challenging, but by analyzing current trends and emerging technologies, we can anticipate the likely tactics and strategies employed against small businesses in 2025 and beyond. This article delves into these trends, offering insights and actionable advice to help small businesses bolster their defenses.

1. The Rise of AI-Powered Ransomware and Automated Attacks:
One of the most significant shifts expected by 2025 is the increased sophistication of ransomware attacks leveraging artificial intelligence (AI). AI can automate various stages of an attack, from identifying vulnerable systems through phishing campaigns to encrypting data and negotiating ransom payments. This automation allows attackers to target a larger number of victims simultaneously with minimal human intervention, significantly increasing their efficiency and profitability.
-
Trick 1: Proactive Threat Hunting: Instead of relying solely on reactive security measures, small businesses should adopt proactive threat hunting strategies. This involves actively searching for malicious activity within their networks, even before an attack occurs. Employing security information and event management (SIEM) systems and utilizing threat intelligence feeds can significantly aid in this process.
-
Trick 2: AI-Powered Security Solutions: The best defense against AI-powered attacks is often another AI. Investing in AI-driven security solutions that can detect and respond to sophisticated threats in real-time is crucial. These solutions can analyze network traffic, identify anomalies, and automatically block malicious activities.
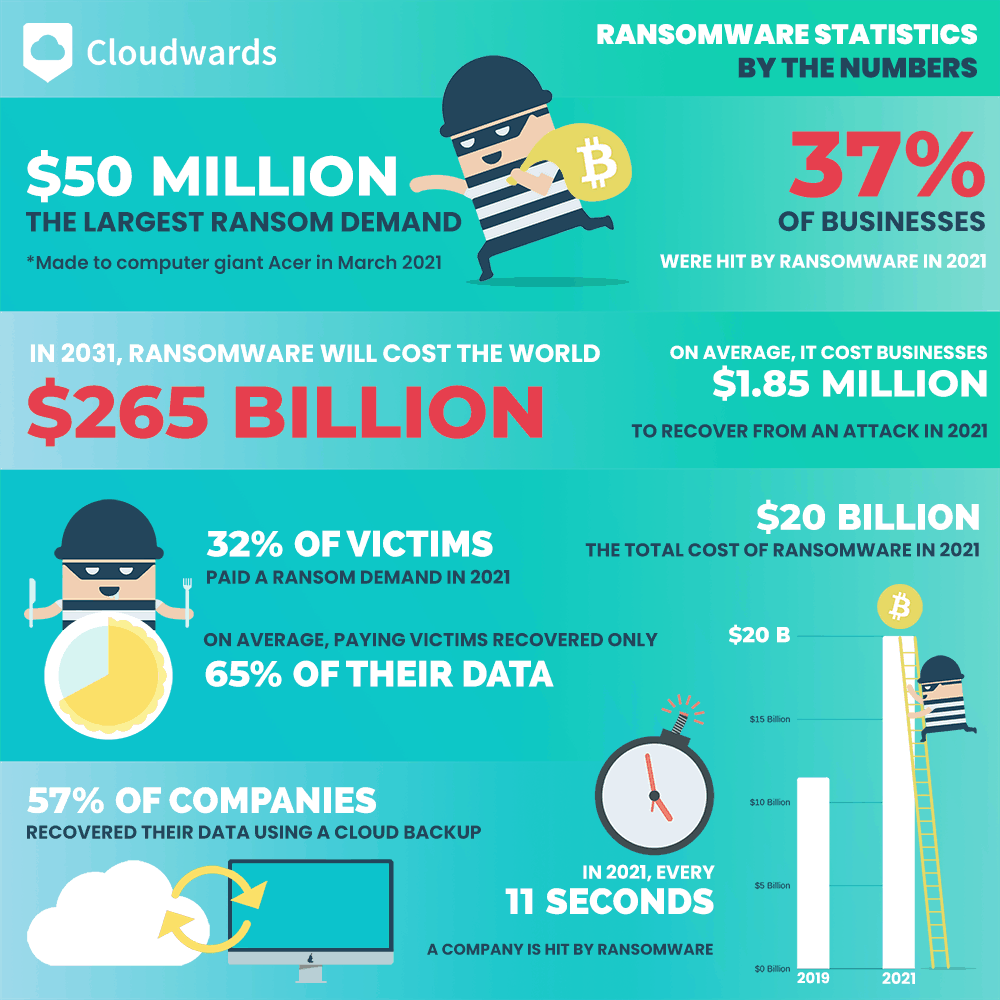
Trick 3: Employee Training on AI-Driven Phishing: AI is also being used to create increasingly convincing phishing emails and other social engineering tactics. Small businesses must invest in robust employee training programs that educate staff on how to identify and avoid these advanced phishing attempts.
2. Extortion Beyond Encryption: Data Exfiltration and Doxing:
Ransomware attacks are evolving beyond simple data encryption. Cybercriminals are increasingly resorting to data exfiltration – stealing sensitive data before encryption – and using it as leverage. This data can then be used for extortion, potentially leading to reputational damage, legal repercussions, and financial losses even if the ransom isn’t paid. The threat of doxing, publicly releasing stolen data, is also becoming more prevalent.
-
Trick 4: Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions: Implementing DLP solutions can help prevent sensitive data from leaving the network. These solutions monitor data movement and block unauthorized transfers, reducing the risk of data exfiltration.
-
Trick 5: Regular Data Backups and Offline Storage: Regular backups are essential, but they must be stored securely and offline. Cloud-based backups, while convenient, can be vulnerable to attack. Consider using an offline storage solution, such as an external hard drive kept in a secure location, to ensure data recovery in case of a ransomware attack.
-
Trick 6: Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly test a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a ransomware attack. This plan should include procedures for containing the attack, recovering data, and communicating with stakeholders.
3. The Growing Use of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS):
The rise of RaaS is lowering the barrier to entry for cybercriminals. RaaS platforms provide malicious actors with readily available ransomware tools and infrastructure, eliminating the need for significant technical expertise. This makes ransomware attacks more accessible to less skilled individuals, increasing the volume and frequency of attacks against small businesses.
-
Trick 7: Vulnerability Management: Regularly scanning for and patching known vulnerabilities in software and operating systems is crucial. RaaS kits often exploit common vulnerabilities, so staying up-to-date with security patches minimizes the attack surface.
-
Trick 8: Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implementing MFA across all accounts and systems significantly enhances security. MFA adds an extra layer of protection, making it much harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access even if they obtain usernames and passwords.
-
Trick 9: Network Segmentation: Segmenting the network into smaller, isolated parts limits the impact of a ransomware attack. If one segment is compromised, the attacker’s ability to spread laterally across the network is restricted.
4. Targeting Supply Chains and Third-Party Vendors:
Small businesses often rely on third-party vendors and suppliers. A breach in a supplier’s systems can provide a pathway for ransomware to infiltrate a small business’s network. This indirect attack vector is becoming increasingly common, highlighting the importance of secure supply chain management.
-
Trick 10: Vendor Risk Management: Establish a robust vendor risk management program to assess the cybersecurity posture of your suppliers. This involves evaluating their security practices, conducting security audits, and requiring them to adhere to certain security standards.
-
Trick 11: Secure Remote Access: If your employees or vendors need remote access to your network, ensure secure access protocols are in place. Utilize VPNs and other secure remote access technologies to protect against unauthorized access.
5. The Exploitation of IoT Devices:
The increasing prevalence of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in small businesses creates new vulnerabilities. Many IoT devices lack robust security features, making them easy targets for attackers to gain access to the network. Ransomware can then spread from these devices to other systems within the business.
- Trick 12: IoT Security Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of your IoT devices to identify any security vulnerabilities. Implement strong passwords, update firmware regularly, and consider isolating IoT devices from the main network to minimize the risk.
6. The Human Element: Social Engineering and Phishing Attacks:
Despite technological advancements, the human element remains a critical vulnerability. Sophisticated phishing attacks, combined with social engineering tactics, can deceive employees into revealing sensitive information or downloading malicious software, providing a direct entry point for ransomware.
-
Trick 13: Enhanced Security Awareness Training: Regular and comprehensive security awareness training for all employees is paramount. This training should focus on identifying phishing attempts, recognizing social engineering tactics, and understanding safe internet practices.
-
Trick 14: Simulated Phishing Attacks: Conduct regular simulated phishing attacks to test employee awareness and identify vulnerabilities in your security training programs.
7. Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) and its Impact on the Future:
The continued growth of RaaS will make ransomware attacks more accessible and frequent. This means small businesses need to be prepared for a higher volume of attacks and potentially more sophisticated techniques. The ease of access provided by RaaS lowers the technical barrier for attackers, meaning even less-skilled individuals can launch devastating attacks.
- Trick 15: Proactive Monitoring and Alerting: Implementing robust security monitoring systems with real-time alerts is crucial to quickly detect and respond to suspicious activity. This includes intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions.
8. The Importance of Cyber Insurance:
While not a direct defense mechanism, cyber insurance can significantly mitigate the financial impact of a ransomware attack. A comprehensive cyber insurance policy can cover costs associated with data recovery, legal fees, and business interruption.
- Trick 16: Comprehensive Cyber Insurance: Small businesses should consider purchasing cyber insurance that covers a wide range of scenarios, including ransomware attacks, data breaches, and business interruption. Ensure the policy adequately covers your specific needs and potential losses.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q: What is the most effective way to prevent a ransomware attack?
A: There’s no single silver bullet, but a layered security approach is most effective. This includes regular software updates, strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, robust backups, employee training, and proactive threat hunting.
Q: Should I pay the ransom?
A: Paying the ransom is generally not recommended. There’s no guarantee that you’ll receive your data back, and paying encourages further attacks. Focus on data recovery from backups and reporting the incident to law enforcement.
Q: How can I tell if I’ve been targeted by a ransomware attack?
A: Signs include unusual system behavior, files being encrypted, ransom notes appearing on your screen, and unusual network activity.
Q: What is the role of cloud security in protecting against ransomware?
A: Cloud security plays a vital role. Cloud-based security solutions can provide enhanced protection, threat detection, and automated response capabilities. However, it’s crucial to choose reputable cloud providers with strong security measures and to configure your cloud environments securely.
Q: How can I improve my employees’ cybersecurity awareness?
A: Regular security awareness training, simulated phishing attacks, and clear communication about security policies are essential. Make cybersecurity a part of your company culture.
Q: What is the cost of implementing these security measures?
A: The cost varies depending on the size of your business and the specific security solutions you choose. However, the cost of a ransomware attack can far outweigh the cost of preventative measures.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of anticipated ransomware trends in 2025 and beyond, targeting small businesses. By proactively implementing these security measures and staying informed about emerging threats, small businesses can significantly reduce their vulnerability to ransomware attacks and protect their valuable data and reputation. Remember, a proactive and layered approach is key to successful cybersecurity.
Source URL: [Insert a relevant source URL here, e.g., a cybersecurity firm’s website or a government agency’s cybersecurity resource page.] For example: https://www.cisa.gov/cybersecurity (This is just an example; please replace with a more specific and relevant source.)
Closure
We hope this article has helped you understand everything about “2025 trends in ransomware attacks targeting small businesses”. Stay tuned for more updates!
Make sure to follow us for more exciting news and reviews.
Feel free to share your experience with “2025 trends in ransomware attacks targeting small businesses” in the comment section.
Keep visiting our website for the latest trends and reviews.
